The area on the right side of the configuration window defines the heart segmentation model applied as well as the sampling method within the segments.
Heart Segmentation Type
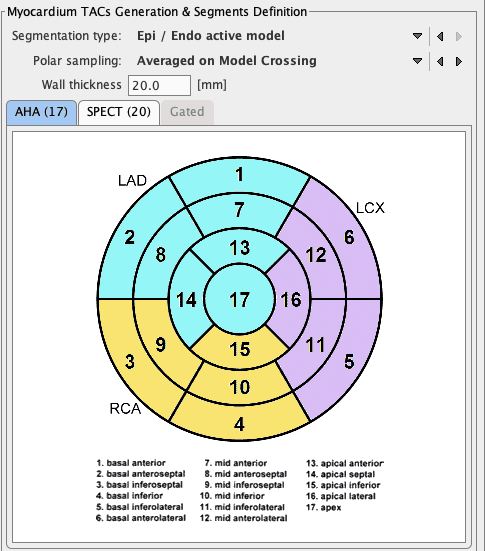
PCARDP supports different segmentation models. Currently, the standard AHA 17-segment model is available, as well as the ASNC 20-segment model which is often used with SPECT data.
CAUTION: A single segmentation must be employed in order to create a normal database, and when comparing subject data against such a database.
There are two options available for the myocardium detection procedure:
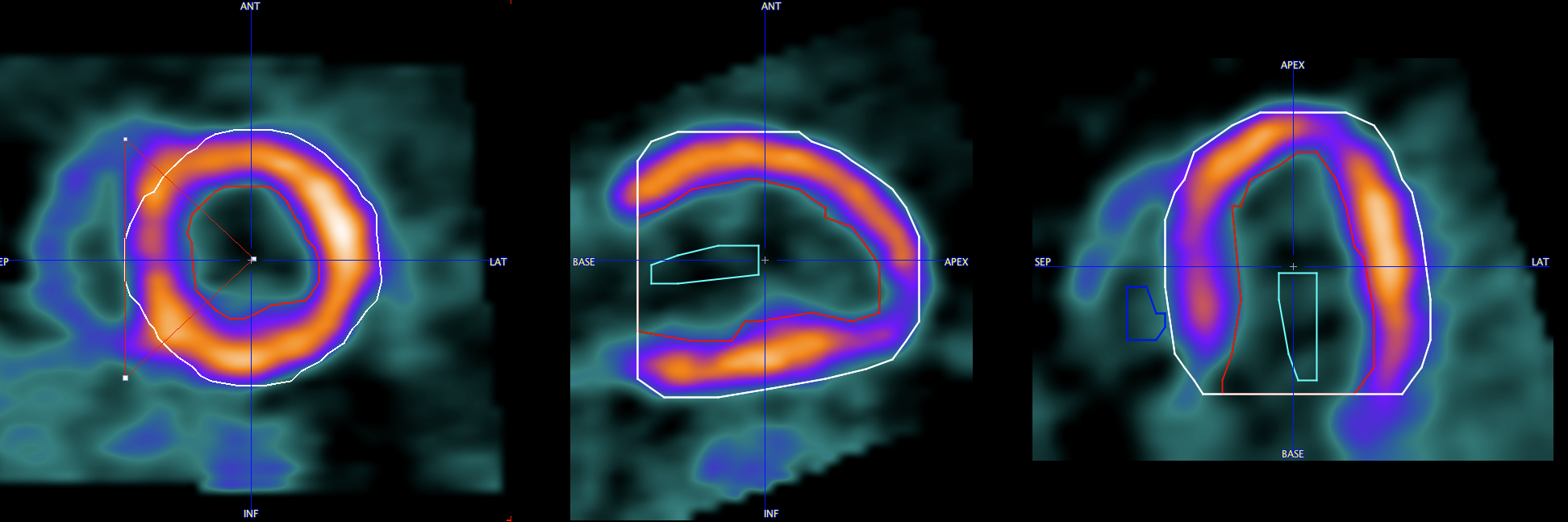
1.EPI/ENDO outline: the myocardium center line is used to generate Epi/Endo contours. Initially, a normal vector is calculated for each vertex of the myocardium center line. Finally, the point belonging to the myocardium center line is translated along the normal vector by half of the heart wall thickness.
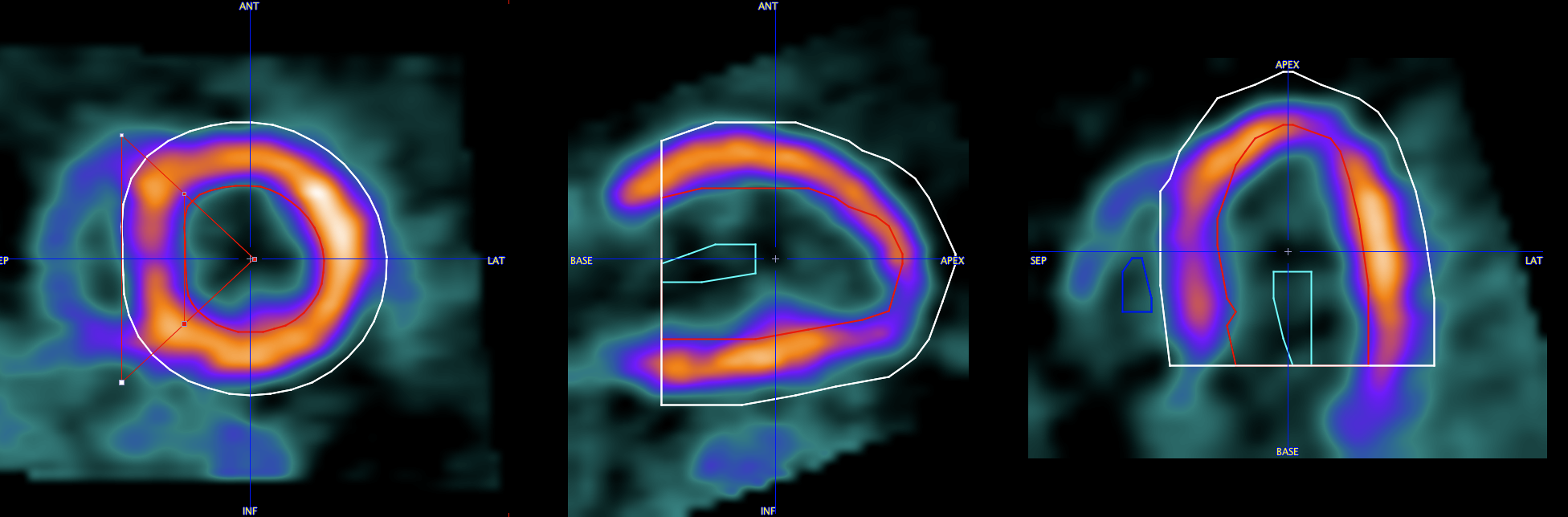
The advantage of the EPI/ENDO definition is that the sampling boundary is very clear and that both contours can individually be adjusted.
2.EPI/ENDO active model: This approach performs first the EPI/ENDO outline, and then adjusts the contours to the local image intensity using an active model (pseudosnake) algorithm.
Polar Sampling
The Polar Sampling selection defines how voxels are sampled within the outlines and used for the segment TAC calculation. PCARDP interpolates the axial range defined by the myocardium model into 22 slices. For each of the base and mid slices a radial sampling is performed every 10°, and a conical sampling in the apical slices. There are different ways how the myocardium samples are detected:
METHOD |
EPI/ENDO outline and EPI/ENDO active model |
Radial Maximum |
The maximum value is determined along the radial profile between the Epi and Endo profiles. |
Model Crossing |
Using the value in the middle between the Epi and Endo shapes. |
Averaged on Model Crossing |
Using a neighborhood of 4 voxels in the middle between the Endo and Epi shapes. |
Averaged on Radial Maximum |
Using a neighborhood of 4 voxels around the determined profile maximum between the Endo and Epi shapes. |
The sampling locations found are not strict pixel locations, but geometrical coordinates. Correspondingly, the program will calculate the image values at the sampling points by interpolation from the neighboring pixels. Radial Maximum is recommended if there is reasonable uptake in tissue, while Model Crossing allows the user to tightly control the sampling, at the cost of having to exactly define the contours.
With the “Averaged on ..” variants more than a single sampling point is determined: the left/right and the inner/outer neighbors will also be included. The suitability of averaging is very depending on the pixel size: if the pixel size is large, the outer/inner samples might add information which is actually outside the myocardium. Therefore, averaging should only be applied with pixel sizes in the range of 2mm.
The thresholded versions of the "Averaged on ..." polar sampling methods are aimed to improve the classification of the voxels belonging to the myocardium. With this selection, initially all the voxels identified as myocardium are sorted in ascending order based on the voxel intensity. Then, a thresholding value is calculated as the 10th percentile of the voxels with the lowest intensity. Finally, only the myocardium voxels which intensity is above the threshold will be considered during the sampling procedure. The thresholded sampling should be used when the segmentation results are poor and when trasmural analysis is performed. However, such segmentation aproaches should be used with caution in cardiomiopathy studies or in case scar tissue is present on myocardium.
Note: the exact sampling points found by a prescribed sampling scheme can be visualized as spheres in a 3D rendering scene (see Examining the Results)
As a means to get a robust global result PCARDP allows averaging the TAC signals from all segments into a single TAC TOTAL MYOCARD. This TAC is only generated, if the box Calculate TAC of total myocardium is checked.
The Baseline correction to first frame box enabled allows correcting the myocardium TACs for the activity remaining from a previous scan.
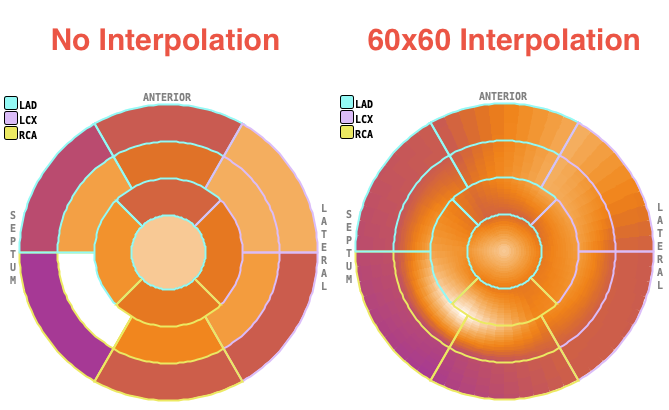
The Polar plot interpolation choice defines how the information calculated in the segments is presented in the polar plots. If it is set to NO, the segment structure is clearly visible. If set to 48x48, values at 48 radial distances and 48 angular increments are interpolated, and similarly with the 60x60 setting. The effect is illustrated in the example below. While the raw polar plot represents the true numbers, the values are smeared by the interpolation filtering.