Texture analysis quantifies the variability of the pixel intensities within a structure such as a tumor. There is a plethora of metrics, which is discussed for instance by Hatt et al. [1] or Sollini et al. [2]. The hope is that (some of) these metrics permit in vivo lesion characterization and provide predictive information about the tumor malignancy.
Rather than calculating hundreds of indexes, the texture analysis implemented in PMOD provides a collection of 64 indexes which have been found to be most valuable in the context of PET imaging. 23 are based on the pixel histogram within a VOI, 25 based on the gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) and 16 based on the gray level run length matrix (RLM). The calculations have been implemented and tested according to the report of the Image Biomarker Standardisation Initiative (IBSI Documentation).
Once the VOIs have been outlined, a texture analysis can be started with the TA action button.
PSEG performs the texture analysis within the VOIs and shows the result in the Texture Analysis page. The controls to the left allow configuring the analysis parameters, and the four panels to the right show information related to the texture calculation.
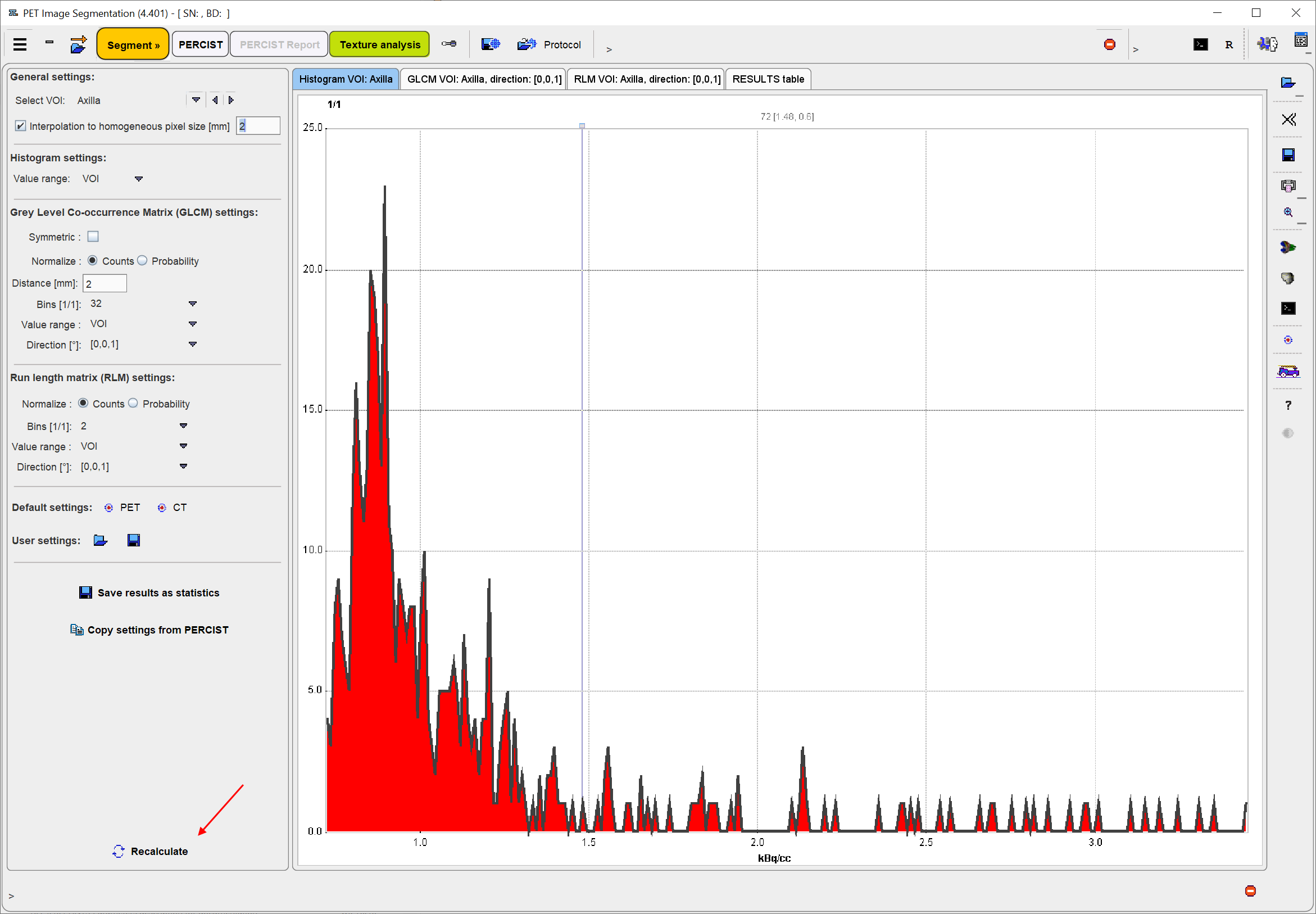
Select VOI allows choosing a representative VOI for which the information in the panels is updated. Interpolation to homogeneous pixel size is recommended for data which doesn't have isotropic resolution, and uses trilinear interpolation.
Histogram Analysis Configuration
The Histogram panel shows the histogram of the values within the selected VOI. The Value range selection defines whether the 256 bins cover the range of the STUDY, the current VOLUME, or just the VOI itself. This will be the input into the histogram-based analysis.
Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) Analysis Configuration
The GLCM calculation is configured on the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix settings: The pixel values are quantized into a small number (N) of discrete values. Similar to the histogram, this process is defined by the specified number of Bins (eg. 32) which cover the range of the STUDY, the current VOLUME, or just the VOI itself, according to the Value range selection.
The occurrence of the quantified values in neighbouring pixels is analyzed, and co-occurrences recorded in a NxN matrix (GLCM): A value i next to a value k will increment the number in the co-occurrence matrix at coordinate (i,k) by 1. If Symmetric is enabled, coordinate (k,i) is incremented as well, producing a symmetric GLCM. A pixel has several neighbors in different Directions at a certain Distance. The co-occurrence can be analyzed in any direction individually. In fact the matrix resulting from the direction specified with the Direction selection is visualized in the GLCM tab. Note, however, that the average matrix of all directions is used for the calculation of the GLCM-based indexes.
Gray Level Run Length Matrix (RLM) Analysis Configuration
The RLM consists of the following steps to be configured on the Run Length Matrix (RLM) settings: As for the GLCM, the pixel values are quantized into a small number (N) of discrete values. A run length is defined as the length of a consecutive sequence of pixels with the same gray level along direction a certain direction.
Texture Calculation
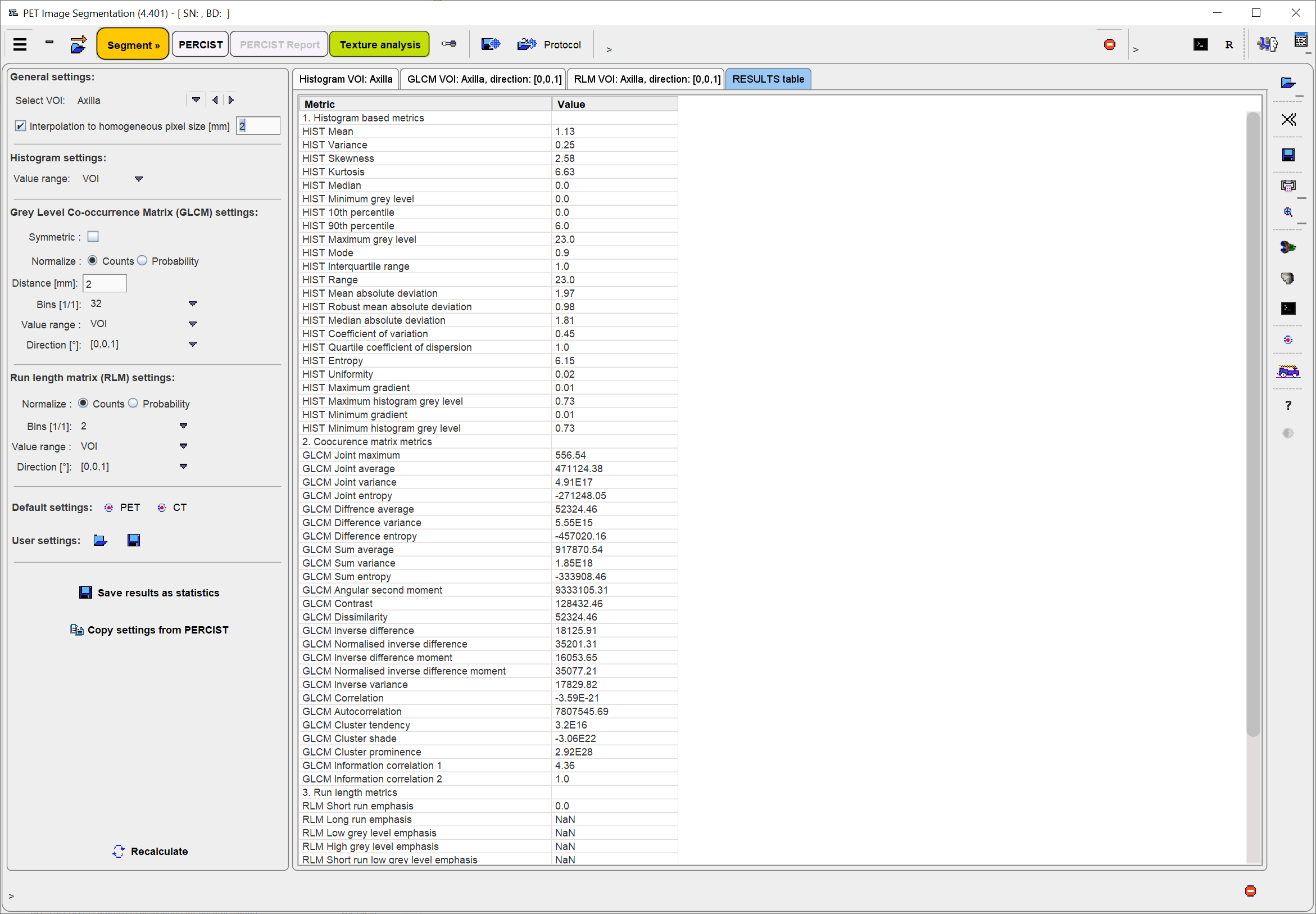
Recalculate initiates calculation of the Histogram and the GLCM/RLM matrices for the VOI with the configured parameters and shows them for preview in the first three panels, and the texture metrics in the RESULTS table.
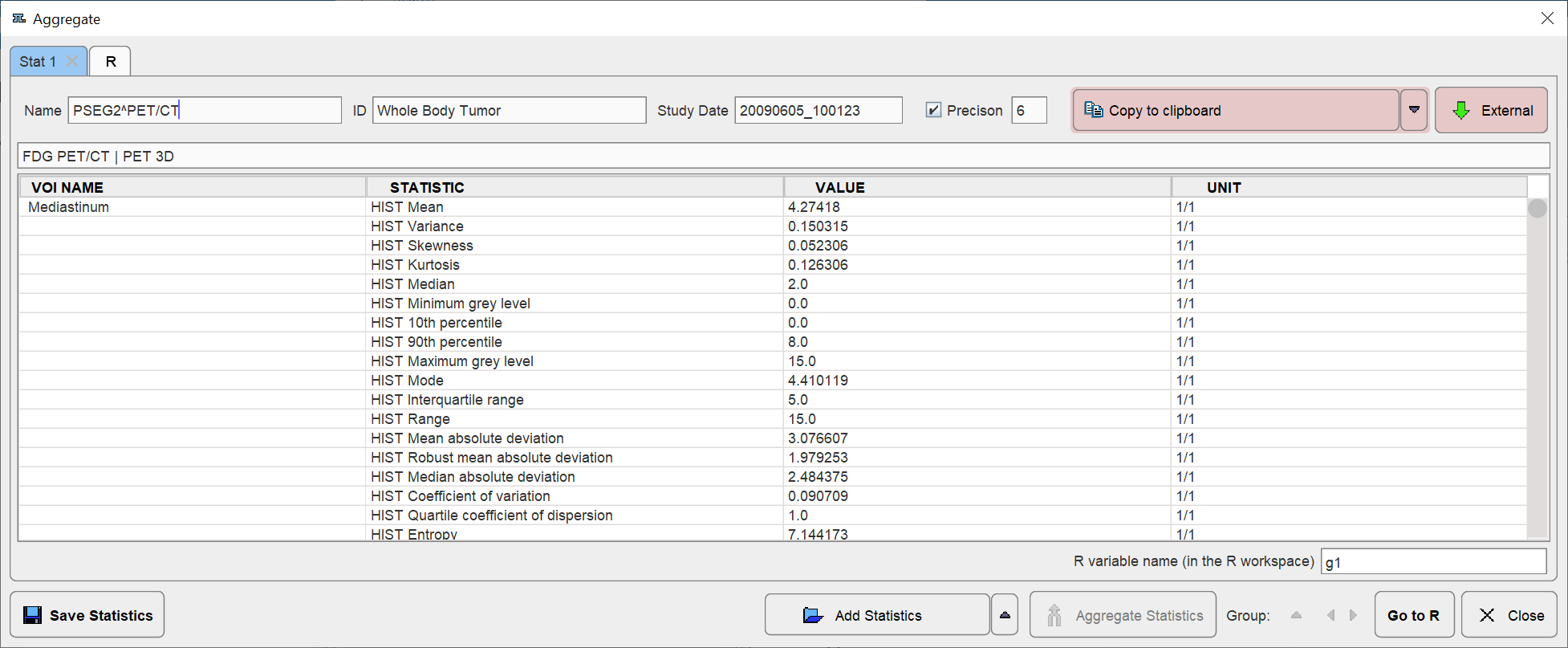
While only one VOI at the time can be evaluated in the user interface, Save results as statistics allows saving the results of all VOIs via the usual PMOD statistics interface illustrated below.
References
1.Hatt M, Tixier F, Pierce L, Kinahan PE, Le Rest CC, Visvikis D: Characterization of PET/CT images using texture analysis: the past, the present... any future? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2017, 44(1):151-165. DOI
2.Sollini M, Cozzi L, Antunovic L, Chiti A, Kirienko M: PET Radiomics in NSCLC: state of the art and a proposal for harmonization of methodology. Scientific reports 2017, 7(1):358. DOI