The purpose of the Preprocessing page is
▪loading images in all kinds of image formats,
▪viewing the loaded images and performing processing operations, and
▪saving (modified) images in one of the supported output formats.
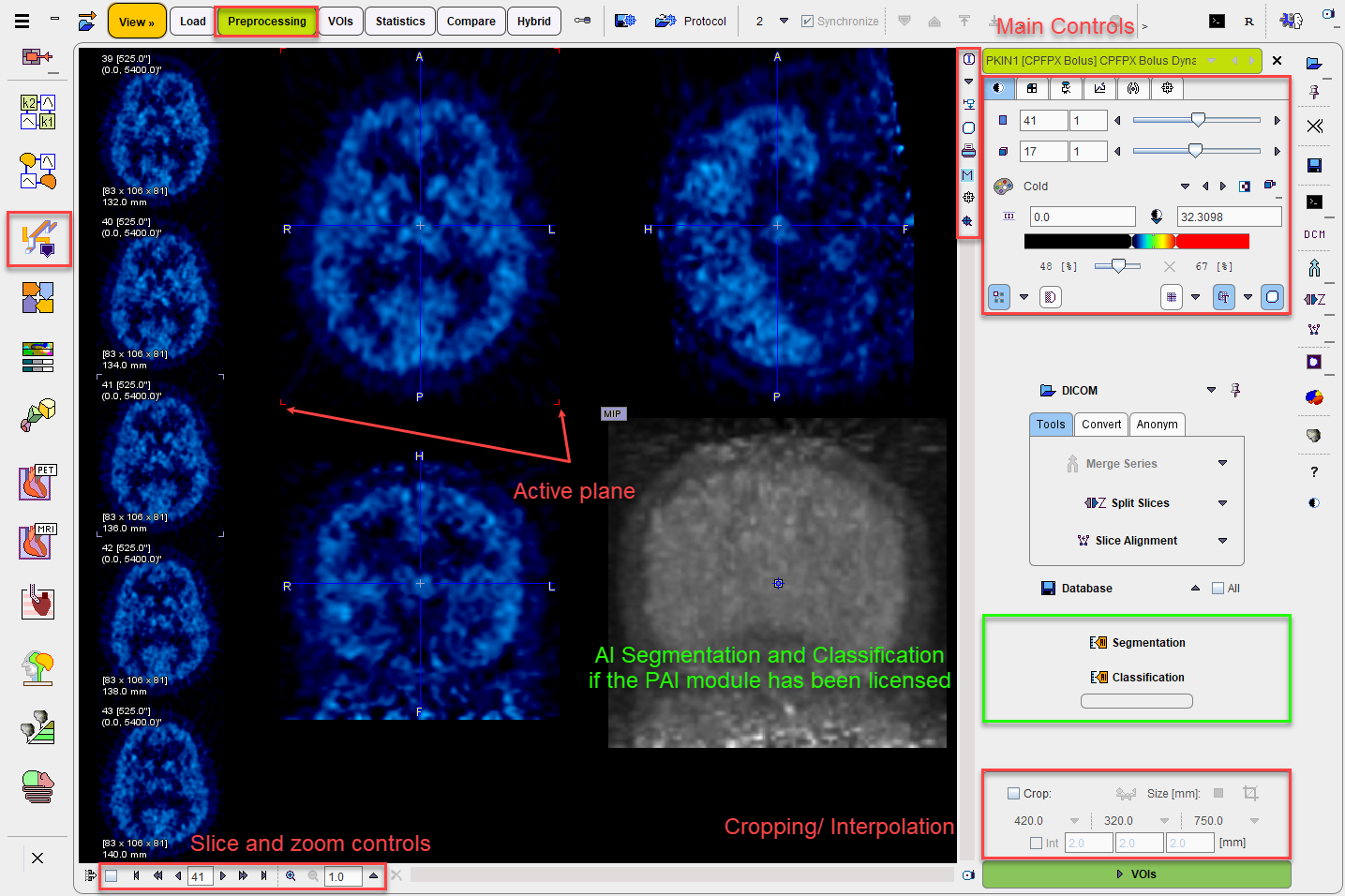
Several images can be loaded, but only one at the time can be viewed on this page. The View page essentially implements the basic PMOD capabilities which are described in the Image Loading and the Image Display sections. Additionally, there are some extra functions available which are accessible by the tabs in the lower right.
Images can be loaded using the Load button or the corresponding icon in the taskbar to the right, whereby the image format is selected using the down arrow. Similarly, images are saved using the Save button or using the icon in the taskbar. The advantage of the latter is that a dialog window is shown to choose the image series and the VOIs list to be saved.
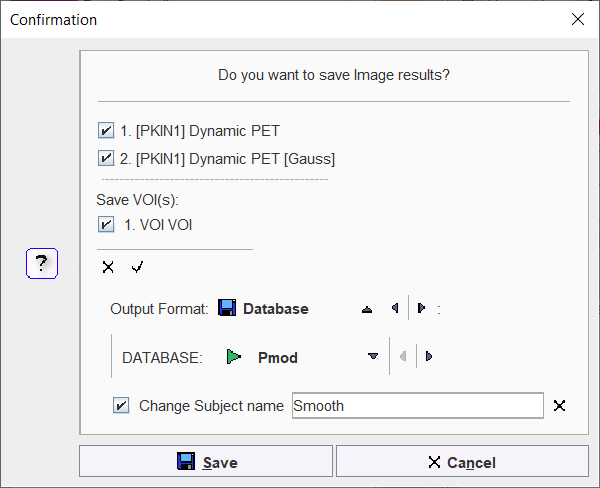
Enabling the Select all icon ![]() has the effect, that all current series and VOIs (if available) are saved when using the Save button. Enable the Change Subject name box to save the image series under a different name.
has the effect, that all current series and VOIs (if available) are saved when using the Save button. Enable the Change Subject name box to save the image series under a different name.
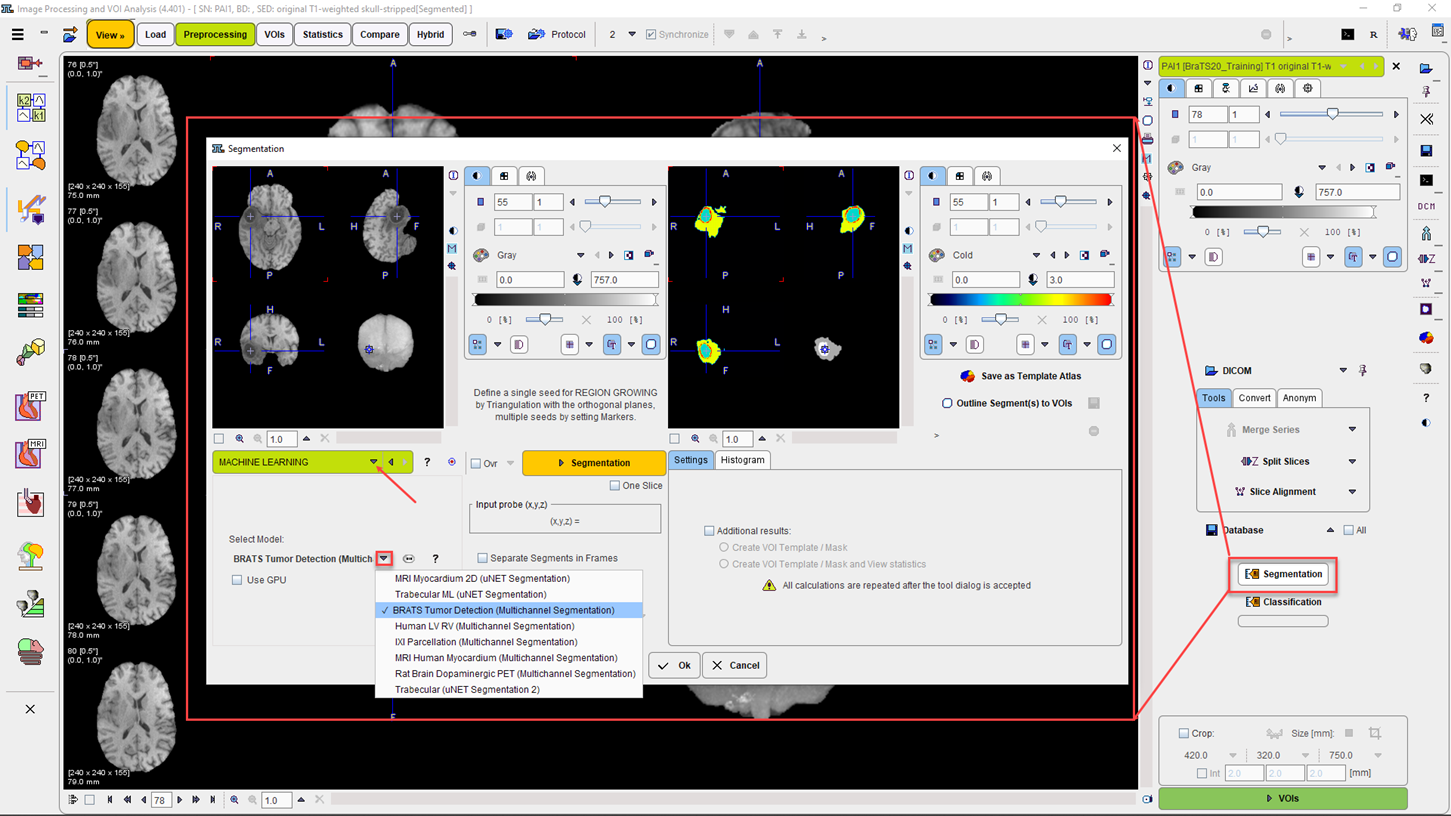
AI Segmentation and Classification shortcut buttons
With the PAI module licensed shortcuts to AI Segmentation and Classification become available on the View page, below the Load/Save section. The Machine Learning is available as an option in the Segmentation interface:
The Learning Sets for AI projects are prepared via the Edit Learning Set(Training) option in the main View menu:
PMOD’s PAI framework aims to make training and deploying ML-based segmentation more accessible to non-expert users. PMOD’s well-tested tools for image processing and traditional segmentation provide an excellent base to prepare the training data needed for supervised machine learning.
In addition to AI-based segmentation, PAI also supports Classification tasks. An example of classification in imaging is the assignment of a label “amyloid positive” or “amyloid negative” to amyloid PET images for tracers such as 11C-PiB. PMOD’s database functionality provides the base to organise data into classes for training of a neural network. The trained neural network then returns the probability of the image to belong to a given class.
Please refer to the dedicated PMOD Artificial Intelligence Framework (PAI) user guide for detailed information about the learning sets preparation, prediction, classification and case studies.
Image Cropping and Interpolation
If the image field-of-view is larger than the structure of interest, the data set should be reduced in order to save RAM and optimize processing. This can be achieved by enabling the Crop box and defining the size of the box which appears as yellow rectangles in the image overlay. Species selection triggers pre-defined sizes for the cropping box.
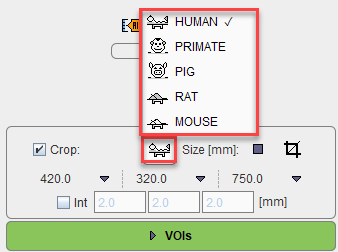
Place the yellow crop box by clicking at the center of the anatomical structure of interest. The structure of interest should be fully enclosed. If this is not the case, the edge size in [mm] can be adjusted for each direction by selecting the size in the corresponding list. An alternative is entering the edge sizes using the button indicated below:
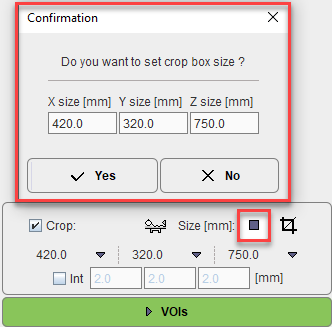
The ![]() button initiates cropping, whereby the original data are replaced. If cropping is not activated manually, a request will be shown when proceeding to the next step. Note: The cropping operation is irreversible and only allowed once.
button initiates cropping, whereby the original data are replaced. If cropping is not activated manually, a request will be shown when proceeding to the next step. Note: The cropping operation is irreversible and only allowed once.
With All input series box enabled the cropping is applied to all images available in the list.
To have a smoother appearance, an interpolation can be configured. To this end, activate the Interpolate box and specify the voxel dimensions in x,y and z in mm.