To define database access for the users, please start the PMOD using the RunPmodClient.bat in the Pmod4.1/Start_CTL sub-directory, and enter the Config menu with the administrator password.
Enabling Database Access for a User
The administrator has to explicitly configure all databases to which a PMOD user has access. This is done on the USERS panel:
1.Select the user, in our example the ATL_Manager.
2.Select the DATABASES tab in the SETTINGS panel.
3.Activate the Add new button to see the list of currently configured databases:
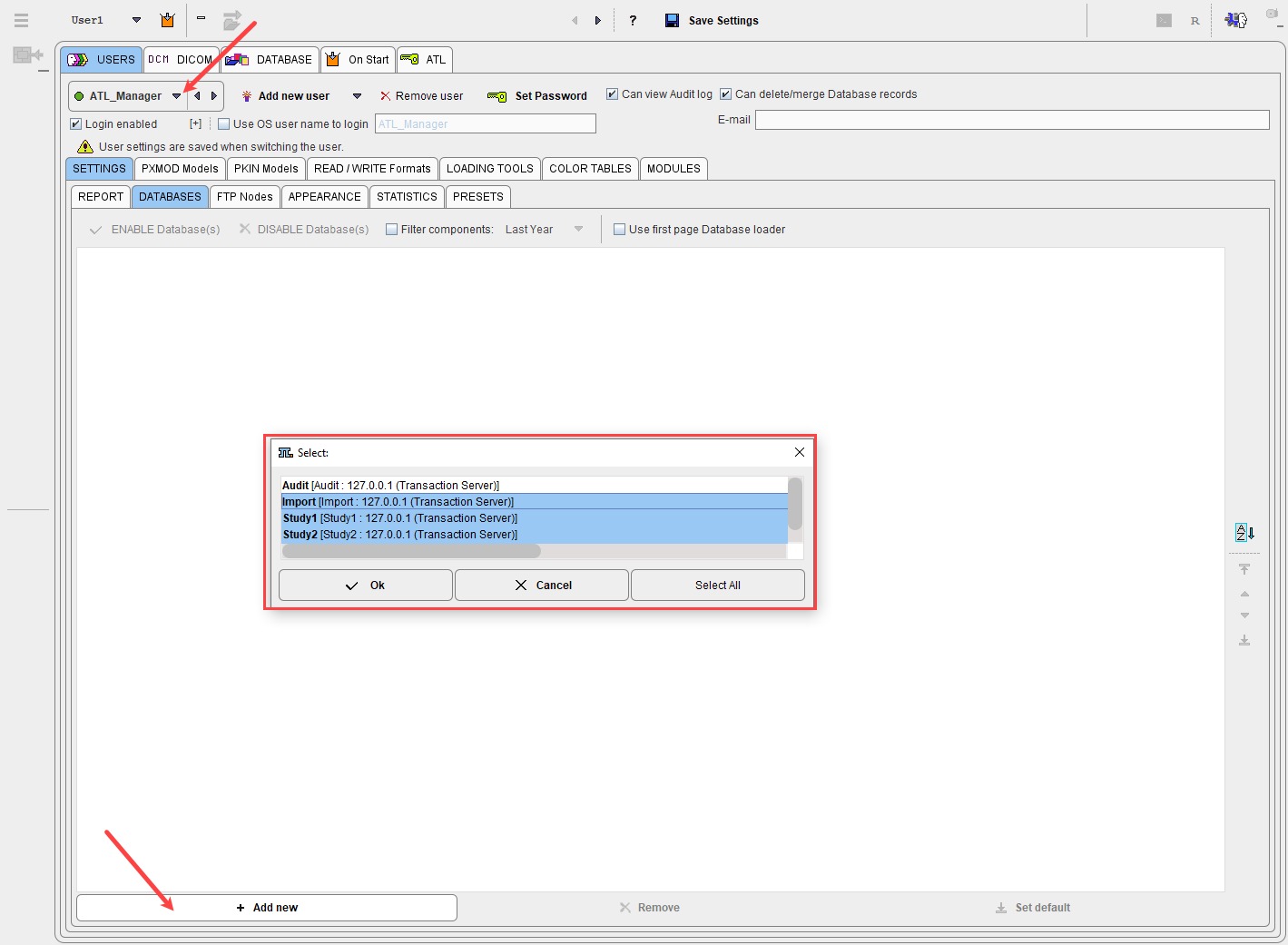
Select the relevant study databases and close with Ok.
4.As a result, the databases to which the user has access are shown in the list with the ENABLED mark.
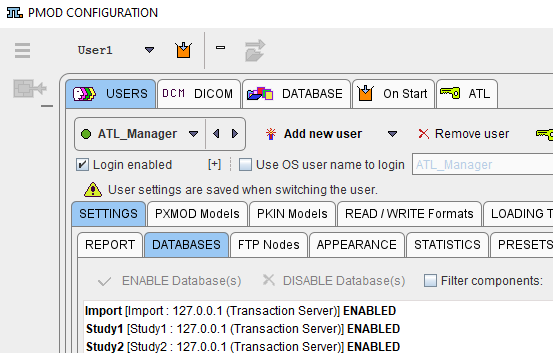
For the user ATL1 enable the Study1 and Study2 databases, and for ATL2 only Study2.
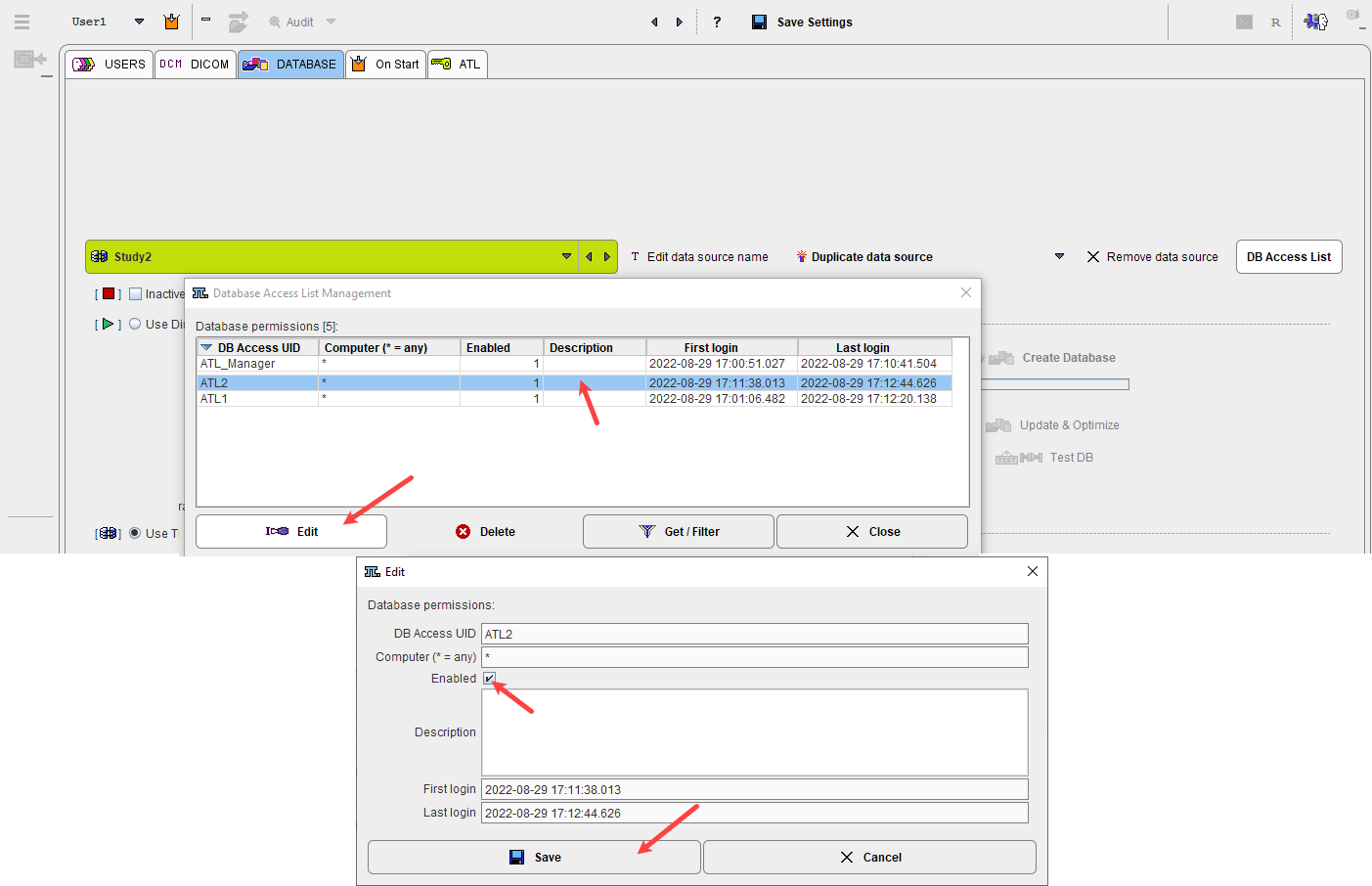
Database Access List
For each database, a user access list is maintained. This list is synchronized with the configuration described above, but provides some more detail.
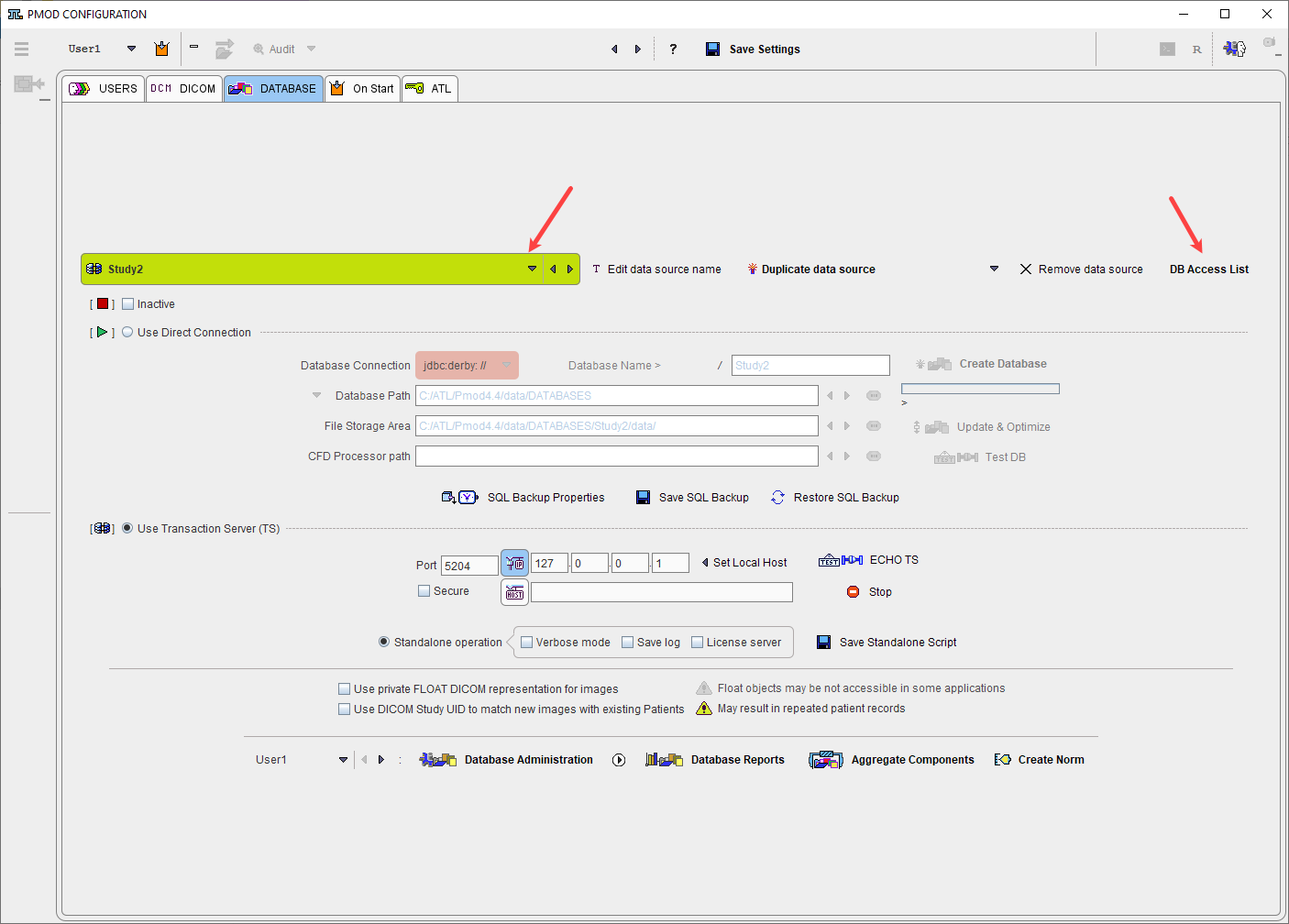
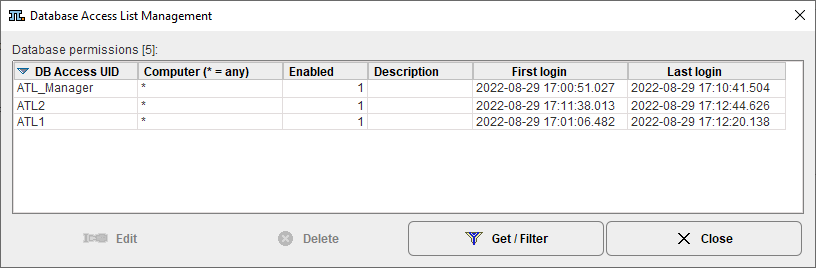
To see and edit the database access lists select the top DATABASE tab of the configuration then the DB Access List button near the data source creation/removal. It shows a dialog window as illustrated below.
The DB Access UID contains the name of the PMOD user. The Computer column shows the systems from which the user can access the database. If the "*" is shown, user access from all client systems are allowed. It can be restricted by replacing * by a computer host name. A value of 0 in the Enabled column indicates that the user has no database access, whereas 1 indicates enabled access. The Description is a convenience field which can be edited by the administrator for commenting purposes. First login and Last login give some information about the activity of the user.
The Edit button serves for editing the selected access list entry as illustrated below. For instance, by removing the Enabled check, the user ATL2 can be blocked from the selected database.