Note that the screenshots in this section illustrate PMOD version 4.3
Image Loading
PSEG does not support the loading of multiple input image series. This is not necessary for AI-based segmentation. In case of a segmentation requiring multiple input images, use the reference for the association list (e.g. T1 MR for the BraTS Tumor Segmentation case study).
Cropping or interpolation in the lower right are generally not required for the AI-based segmentation workflow. This will be done by the model depending on the preprocessing parameters used in the Learning Set. Cropping may be used when the image field-of-view is clearly larger than the scope of the model. For example, an MR image of the human head including neck may be cropped to brain only for the IXI Parcellation model (human brain MR deep nuclei segmentation, see Case Study). Masking is not required for AI-based segmentation. We recommend using the shortcut AI Segmentation to skip to the next step in the workflow:
Model Selection
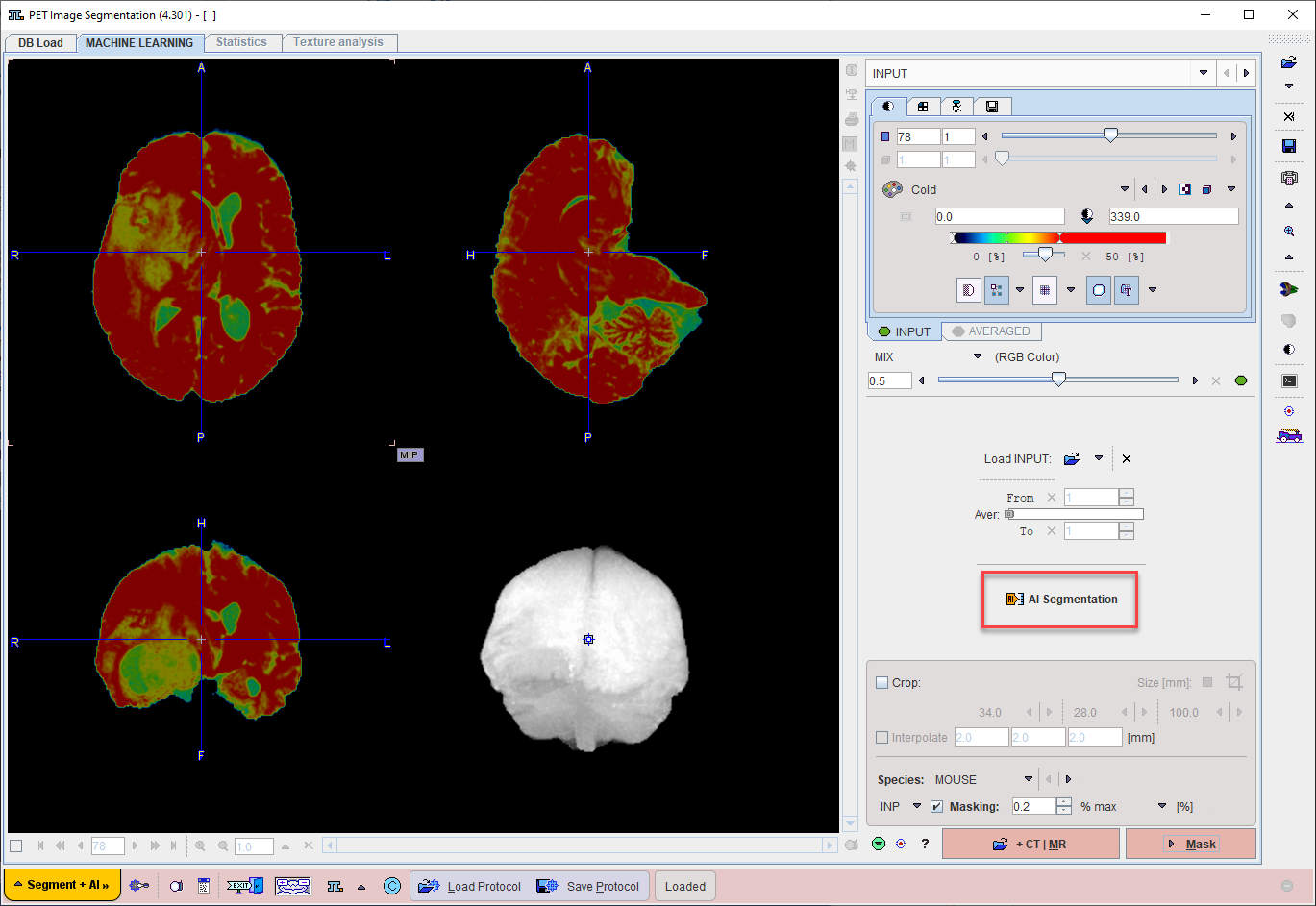
On the MASK page set the segmentation method is set to MACHINE LEARNING.
Choose the appropriate model for the segmentation task using the menu Select Model.
Self-trained models may be selected using the AI Learning Set browser. Note that a description of the model can be retrieved using the PAI Model Help button:
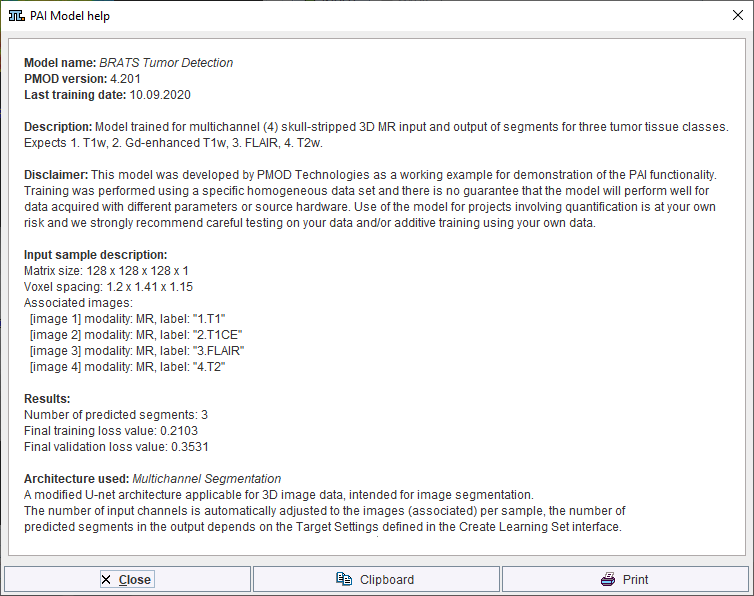
Note that the available text shown is controlled by the user for self-trained models during creation of the Learning Set (and architecture Python files if applicable).
Displaying the R Console during prediction is optional, according to the checkbox selection Show R Console.
Segmentation
Use the Segmentation workflow button to start prediction. The input data is transferred to the R Console and processed using the selected model.
The segmentation result is overlaid on the input series on the SEGMENTS page.
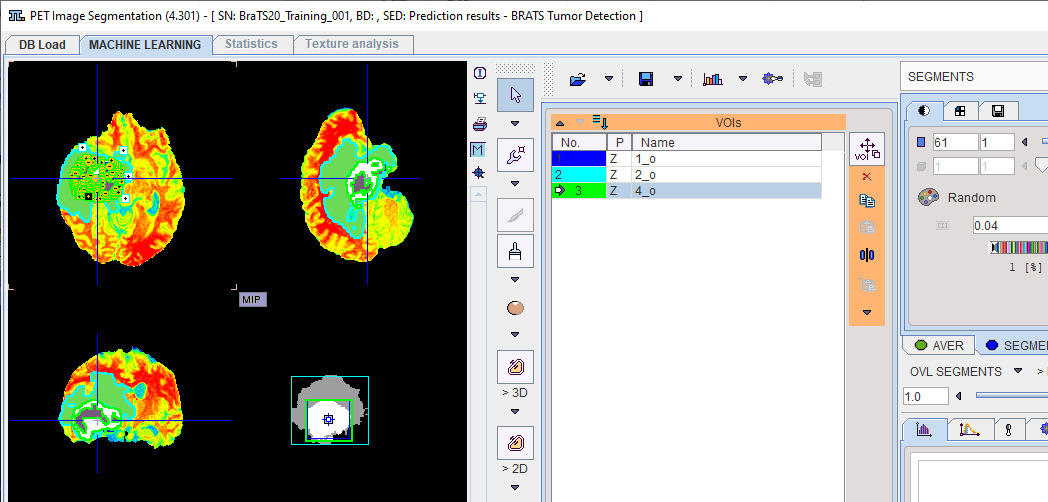
The segments are automatically converted into numbered VOIs. The interactive VOI labeling function is still available by right-clicking a segment in the image. This opens a dialog window which allows a VOI name to be selected from a list, or simply entered. Note that the VOI name from list functionality is also available via VOI Properties.
The segments label map itself can be saved using the save button in the taskbar to the right.
Please refer to the PSEG User Guide for details of the general segmentation functionality.
At the end of processing the protocol can be saved using Save Protocol. Using Load Protocol the workflow can be retrieved and re-executed. Additionally, the input series can be changed and the protocol used for analysis of the next sample. Protocols also provide access to batch processing.
Batch Processing
A saved protocol is required to start batch processing. This saved protocol provides the settings that will be used for the workflow across all samples. A set of saved protocols can be loaded using Set Files, or more commonly a single protocol describing the desired workflow can be cloned for all input samples using Clone Protocols.
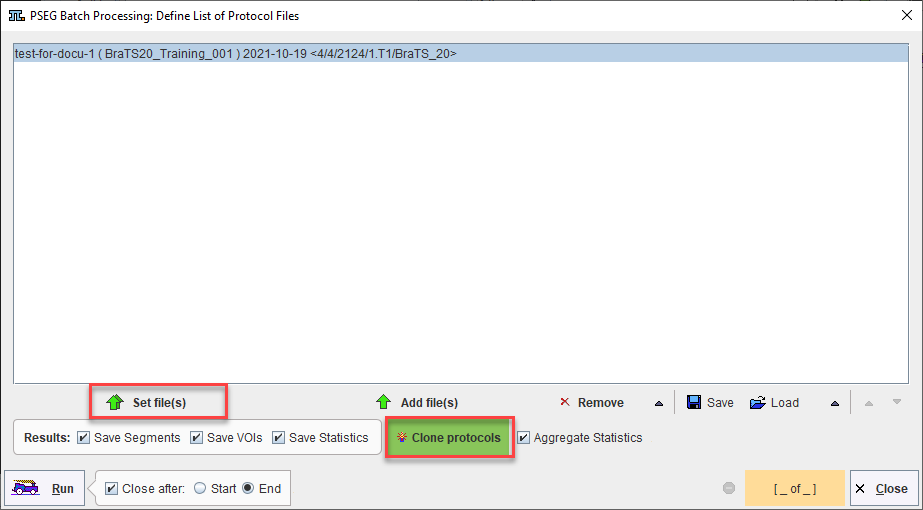
Clone Protocols opens a dialog window in which a list of input samples should be provided using Set Files. In the case of AI segmentation tasks that require multiple input series, the reference for the association list should be selected. PMOD will automatically retrieve the other associated series for processing. The flat view for the database and advanced database queries can be useful to select all input series for batch processing efficiently.
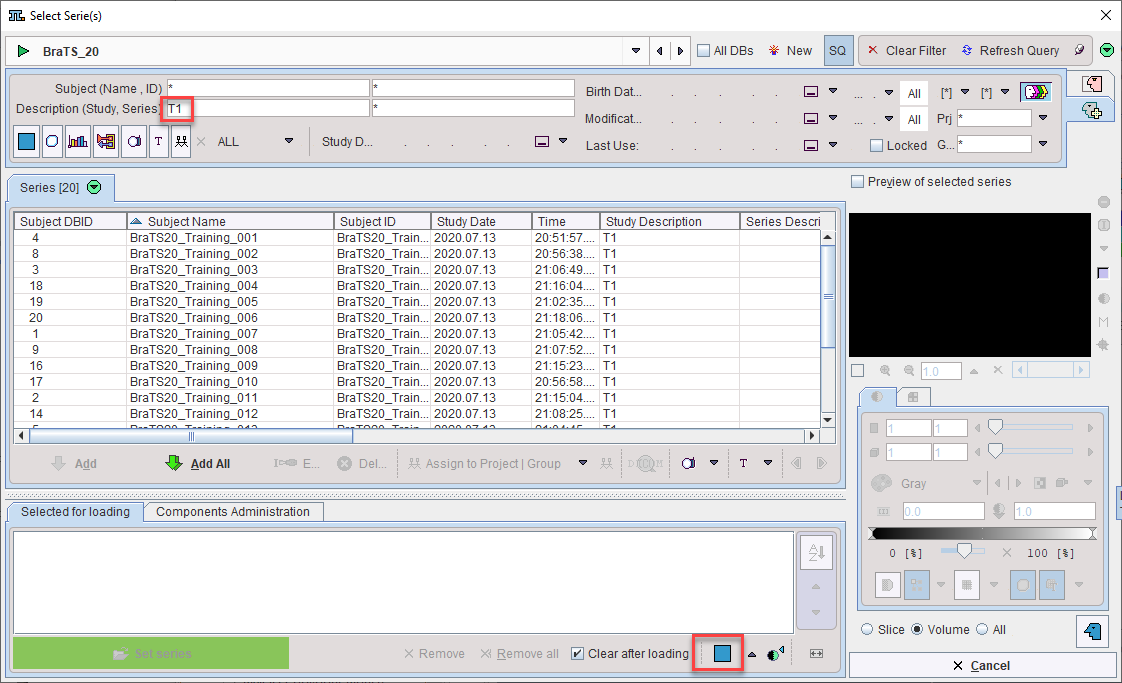
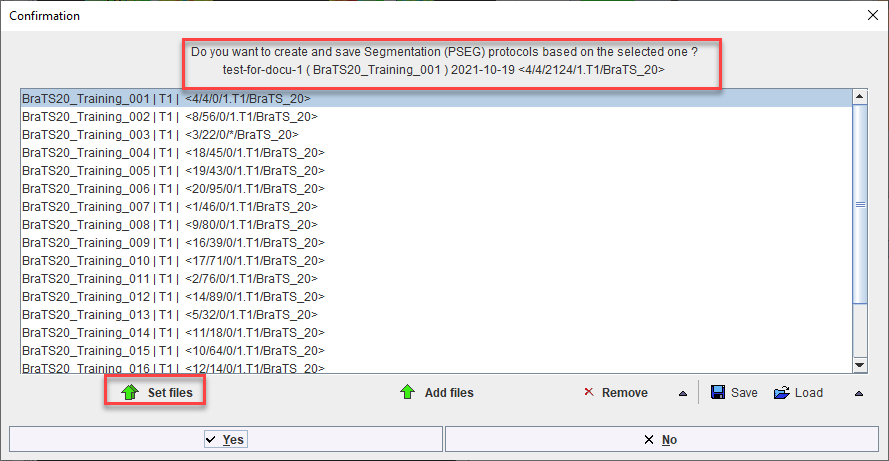
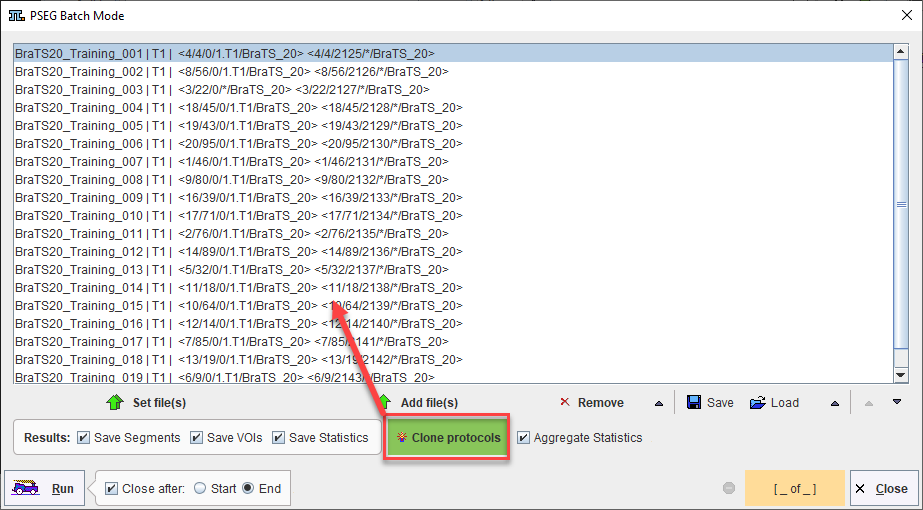
Once the desired list of protocols has been loaded or generated through cloning, batch processing can be launched using the Run button. Results will be saved in the same location as the input data - we strongly recommend using the database.