Cardiac MR cine acquisitions are widely used to assess left ventricular function, using the evolution of left ventricle volume over the cardiac cycle to calculate parameters such as systolic/diastolic volume, ejection fraction and cardiac output (if frame timing is provided corresponding to the actual duration of the cardiac cycle).
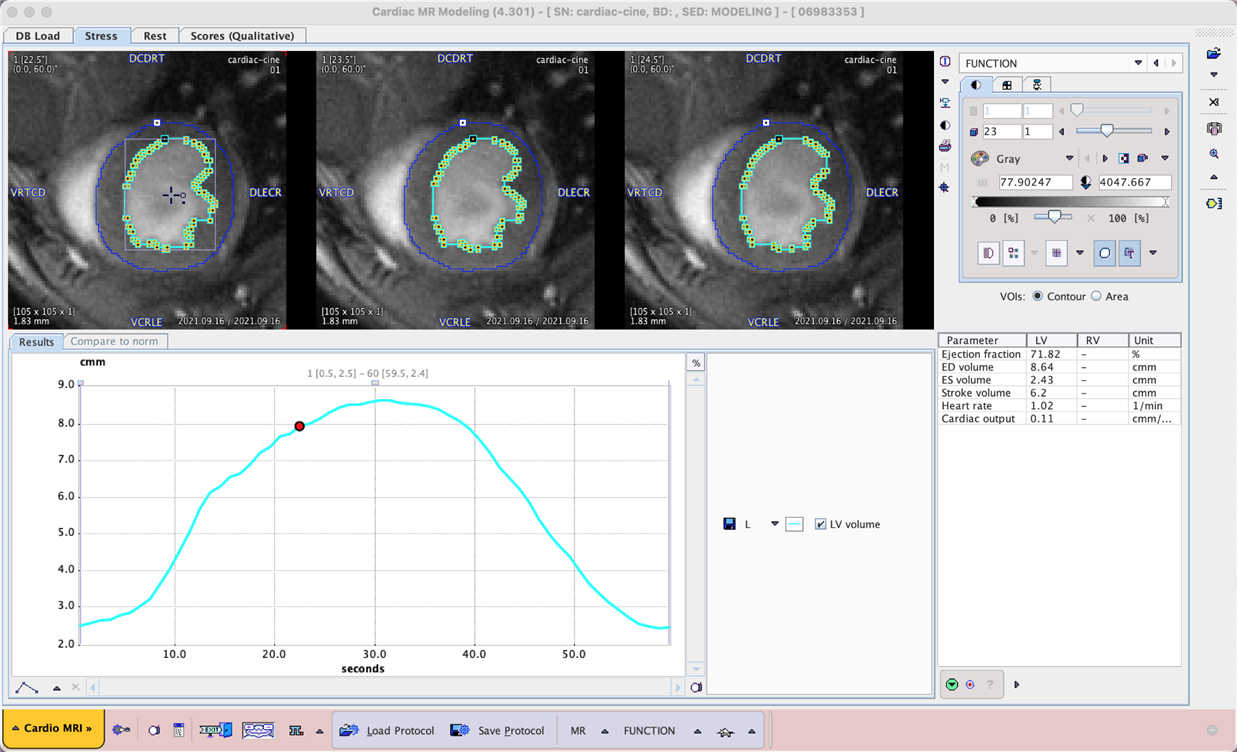
Manual delineation of the left ventricle is subjective and can be time consuming in case of many cine frames and/or multislice acquisitions. Automatic methods may be limited in success due to variable acquisition parameters, image contrast and noise, as well as artefacts due to swirling blood in the ventricle.
We hypothesised that AI-based segmentation could provide a useful alternative to these methods.
Example data to test the MRI Myocardium 2D and MRI Human Myocardium models is available in our Demo database (Subjects PAI2 and PAI3). The data used for the case study was provided by Bruker colleagues and in a private collaboration.
To try the models for yourself we recommend use of the Cardiac MR Modeling tool (PCARDM) FUNCTION workflow. See the specific documentation for PCARDM. The model selection is determined by the species selection in PCARDM. The models were trained with 2D data so Split Slices and Split Frames are required. The recommended Heart Box for example PAI2 is 10 x 10 mm, and for PAI3 100 x 100 mm. The data used in these cases was for a limited range of MR sequences - the performance of the model may vary for data from different hardware and/or with different contrast/pre-processing.