PET images are inherently affected by the partial-volume effect. This means that the measured tracer activity concentration is not accurate due to the relatively low image resolution and the limited tissue sampling. The low spatial resolution of the PET system causes a blurring of the image, so that high activities (from a hot lesion) are spread to the surrounding as illustrated below. This effect is called spill-out. The same effect also causes a spill-in of background activity into the volume of interest.
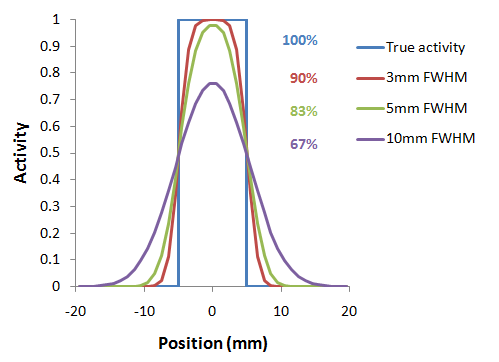
As a consequence, hot lesions tend to appear less aggressive (reduced maximum) but bigger (spreading) than they are in reality.
Spill-in and spill-out depend on the geometry of the objects, the activity distribution of the tracer, and on the resolution of the scanner which may vary across the imaging field-of-view. Therefore, practical correction approaches have to assume certain conditions and can only be approximate. For a nice overview of the topic please refer to the publication of Soret et al. [1].
Partial-volume correction in PNEURO is accessed on the VOIs page of either the Maximum Probability Atlas or Brain Parcellation workflows:
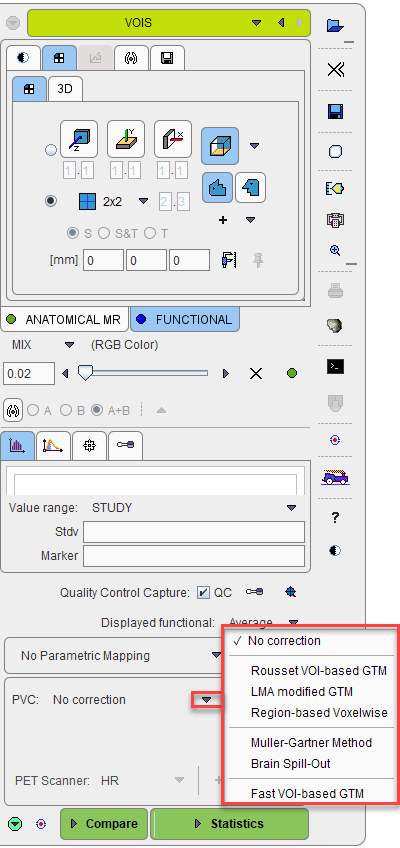
The selection and configuration of the methods available is described in more detail in the Workflow sections of this document.
Complementary VOIs
After the PVC correction is performed a list of complementary VOIs appears on the Group list under the Complementar branch.
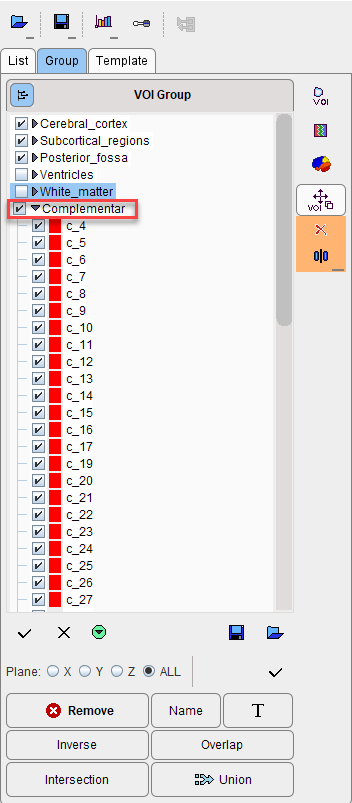
The Complementar VOIs are representing the regions that were masked out during the intersection of the Atlas structures with the grey/white matter segmentation. These VOIs were created since the very beginning and were generated in order to meet the conditions of the GTM correction method: the area is divided into homogenous regions covering as much as possible. Empty spaces between the corrected VOIs would cause inaccurate correction.
The availability of these VOIs on the list after running the PVC is aimed to increased the transparency such that they can be saved and used for the exact reproduction via the Protocol.
When a PVC method is used, both the original and the corrected statistics are calculated. Note that due to the high number of VOIs the PVC calculation may take several minutes and consumes a significant amount of RAM.
Note:
The PVC is always calculated for all the created VOIs but statistics results are returned only for the VOIs that are selected on the Group tab.
When Parametric mapping is enabled, only three PVC methods are available for selection: Region-based Voxelwise, Muller Gartner Method and Brain Spill-Out.