The stereotactic normalization to be used for the database is defined on the 3. Spatial Normalization tab.
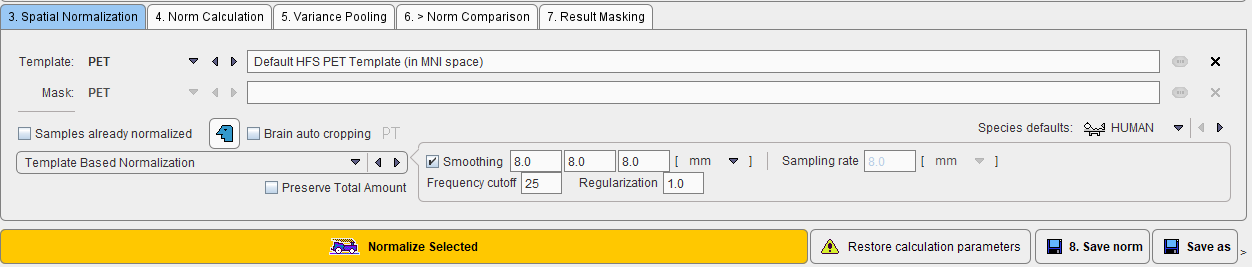
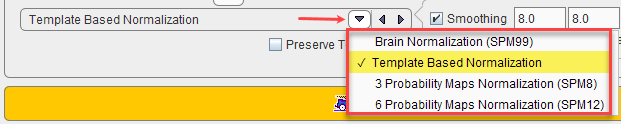
The main choice is selection of the spatial normalization procedure.
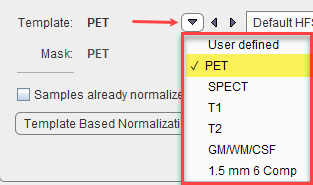
and a corresponding template image.
Normalization Methods
The normalization procedures are summarized below. The parameter presets are species dependent and can be set using the Species defaults selection. If the image field-of-view is significantly larger than the brain, Brain auto cropping ![]() should be enabled, and the proper modality (PT, MR) set. If the data are not available in the HFS orientation, the button left of Brain auto cropping
should be enabled, and the proper modality (PT, MR) set. If the data are not available in the HFS orientation, the button left of Brain auto cropping ![]() should be enabled to automatically perform the reorientation.
should be enabled to automatically perform the reorientation.
Normalization methods:
Brain Normalization (SPM99) |
SPM99-type normalization with parameters Because the normalization template is typically a relatively smooth image, some smoothing of the target image is needed to make it more similar to the template. To this end a Gaussian smoothing filter may be defined by its full width at half maximum in all directions (x,y,z). No. of Basis Functions from the cosine transformation in each direction. Suitable template images are the PET and SPECT templates in the MNI space, or a proprietary User defined template image. |
Template-based Normalization |
SPM5-type normalization with the same template images as above. Based on the Gaussian smoothing as above, the Sampling rate is determined. Alternatively, Gaussian smoothing can be disabled and a dedicated Sampling rate specified. The specified Frequency cutoff (default = 25) is used for calculating the number of basis functions. Higher cutoff values result in fewer basis functions. Regularization controls the smoothness of the deformation field. The higher regularization, the smoother the deformation. |
3 Probability Maps Normalization |
Normalization applicable to 3D T1-weighted MR images ( parameters ) It uses the normalization resulting from the SPM8-type unified MR segmentation and requires the G + W + F template, which is automatically selected. |
6 Probability Maps Normalization |
Normalization applicable to 3D T1-weighted MR images with ( parameters ) It uses the normalization resulting from the SPM12-type unified MR segmentation and requires the 1.5 mm 6 Comp template, which is automatically selected. |
With User defined templates please use the ![]() button to select the template image, which must be available in the database. For new tracers, the user may first have to generate a suitable template outside PNEURO and import it into the database.
button to select the template image, which must be available in the database. For new tracers, the user may first have to generate a suitable template outside PNEURO and import it into the database.
A mask is required to cut off signal from outside the brain during the normalization. It is specified using the Mask selection. While the standard templates already have associated mask files for use during normalization, User defined templates require specification of a dedicated Mask series in the database.
The Preserve Total Amount option enables volume modulation during image reslicing as used for VBM applications (Voxel Based Morphometry). Rather than preserving the concentration in the image, the total amount is preserved.
Normalization of the Control Images
After the normalization method has been fully specified, the samples in the list can be selected and their normalization started with the Normalize Selected button.
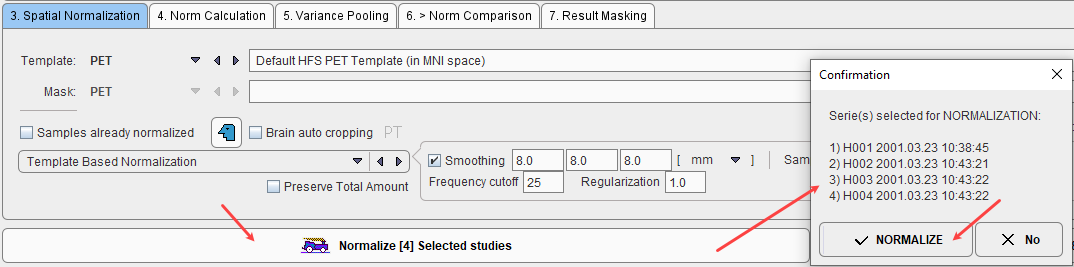
The normalization is performed in the background, and finally confirmed by a message. The normalized images are saved in the database as new series of the controls, labeled with NORMALIZED in the series description. Although smoothing is applied during the process of normalization, the NORMALIZED images are not smoothed. Sample images which have been normalized are marked in the Samples list with the ![]() symbol.
symbol.
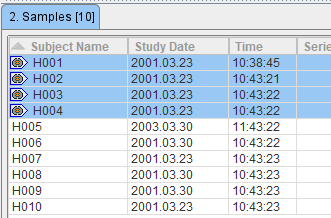
When creating a Brain Norm it is important to ensure that only correctly normalized samples without truncated areas are included. Although a certain inaccuracy of the mapping from the subject anatomy to the stereotactic template cannot be avoided, samples showing gross deviations should be excluded from the analysis.
A fusion display supporting the quality control of spatial normalization is integrated in the Edit Norm tool. When the Preview box is checked and the Validate Normalized tab is selected, the image display shows a fusion of the template with the normalized sample image.
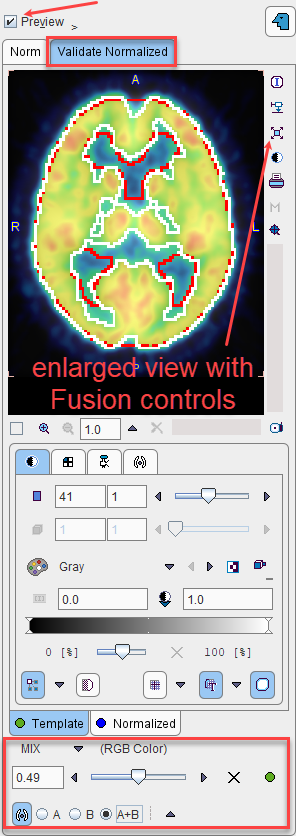
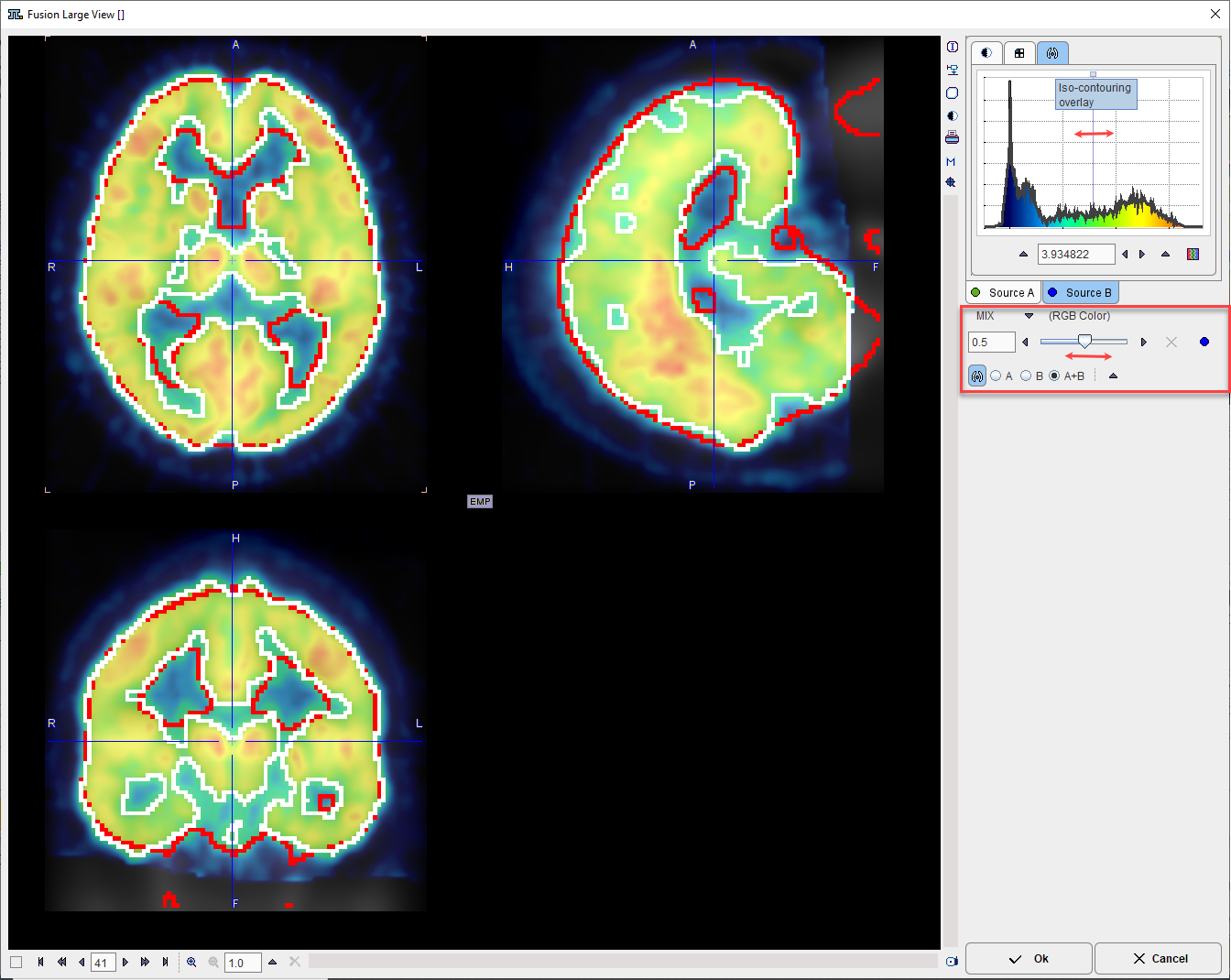
The tabs allow switching between the Template and Normalized images, for example to adjust the color tables or to define the iso-contour level. The relative contribution of the two components to the fusion image is governed by the fusion balance slider.
The easiest way to quickly check all normalized samples in the database is to switch to the orthogonal view of the Validate Normalized tab, select the first entry in the 2. Samples list, and with the ARROW DOWN keyboard key browse through the list entries. Each time a new sample is selected the view gets updated.
For a detailed analysis the fusion display can be blown up using the large view button indicated above.
Already Normalized Control Images
A special case is the use of control images which have already been normalized externally and saved in the database, for instance during the Maximum Probability workflow of PNEURO. Note that such images have to be calculated in the space of the atlas which is used in the Brain Norm workflow.
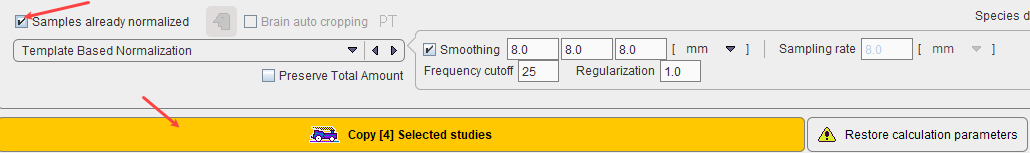
The flag Samples already normalized allows indicating this situation. As a consequence, normalization of the control data is not necessary, and therefore the button Normalize Selected study changes to Copy Selected study as illustrated below. Note that the normalization definition is still required to normalize test subject images for comparison with the Brain Norm.