The irreversible 2-tissue compartment model separates tracer in tissue into two exchanging compartments C1 and C2 with a serial structure. The arterial plasma exchanges with the first tissue compartment C1, which in turn exchanges with the second tissue compartment C2 where the tracer is trapped. K1 [ml/ccm/min] and k2 [1/min] are the uptake and clearance rate constants, whereas k3 [1/min] describes the trapping. The usual interpretation is that C1 represents free and non-specifically bound tracer in tissue (non-displaceable compartment), and C2 irreversibly bound or metabolized tracer.
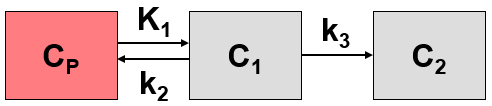
An important parameter of an irreversible configuration is net influx rate Ki, the unidirectional uptake rate constant that incorporates both net inward transport and trapping of the tracer in tissue.
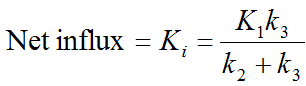
Another macroparameter "lambda*k3" as been used in the context of enzymatic reactions, where k3 is supposed to be proportional to enzyme concentration.
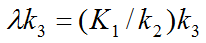
Logan et al. [1] have shown in simulations that lambda*k3 is preferable to k3 alone in terms of bias and precision.
Differential Equation of the Mass Balance
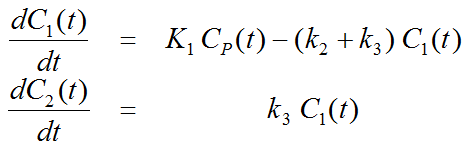
with input curve Cp(t).
Operational Model Curve
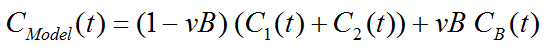
with the concentration CB(t) of tracer in whole blood, and the blood volume fraction vB.
Parameter Fitting
The model includes the 4 fitable parameters vB, K1, k2, k3, and calculates the macroparameter Flux. Usually, vB is fixed at a physiologic value of 3-5% to reduce the number of fitted parameters. An alternative is to fit vB with a TAC from a big representative VOI, and fix it for the TACs from smaller VOIs.
Alternative Models with Flux Fit Parameter
There are two alternative models available which have the same structure but use the Flux as a fit parameter. The advantage of the reformulation is that the Flux can be calculated with the robust Patlak model, and used as a fixed parameter in the compartment model fit.
Reference
1.Logan J, Fowler JS, Ding YS, Franceschi D, Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Felder C, Alexoff D: Strategy for the formation of parametric images under conditions of low injected radioactivity applied to PET studies with the irreversible monoamine oxidase A tracers [11C]clorgyline and deuterium-substituted [11C]clorgyline. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002, 22(11):1367-1376. DOI