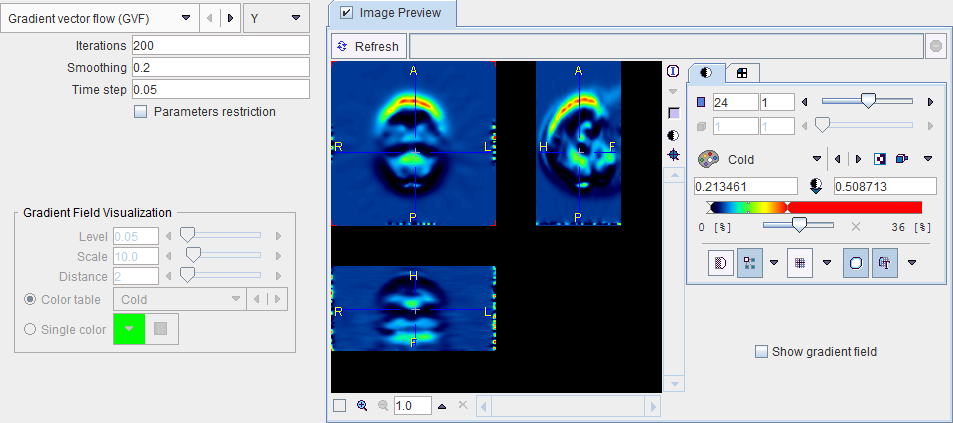
The Gradient Vector Flow tool allows calculating the image gradient in a specified direction [1], which is for instance used for active contours algorithms.
Different algorithms are supported:
▪GVF: calculates the gradient using the gradient vector flow algorithm;
▪General GVF: calculates the gradient using a generalized gradient vector flow algorithm;
▪Differential gradient: calculates the gradient by subtracting values of neighbouring pixels;
▪Sobel operator: calculates the gradient by convolving filter mask with matrix consisting of image pixels.
During the estimation procedure the following parameters can be set:
▪Gradient width: distance (in pixels) between two points, the intensity difference which defines the gradient value;
▪Iterations: number of iterations performed during GVF and GGVF calculation;
▪Smoothing parameter (μ): regularization parameter governing the trade-off between the first and the second integral term. Smoothing parameters should be set according to the amount of noise present in the image: the higher the noise the bigger the value.
▪Time step (Δ): is representing the time length for each iteration.
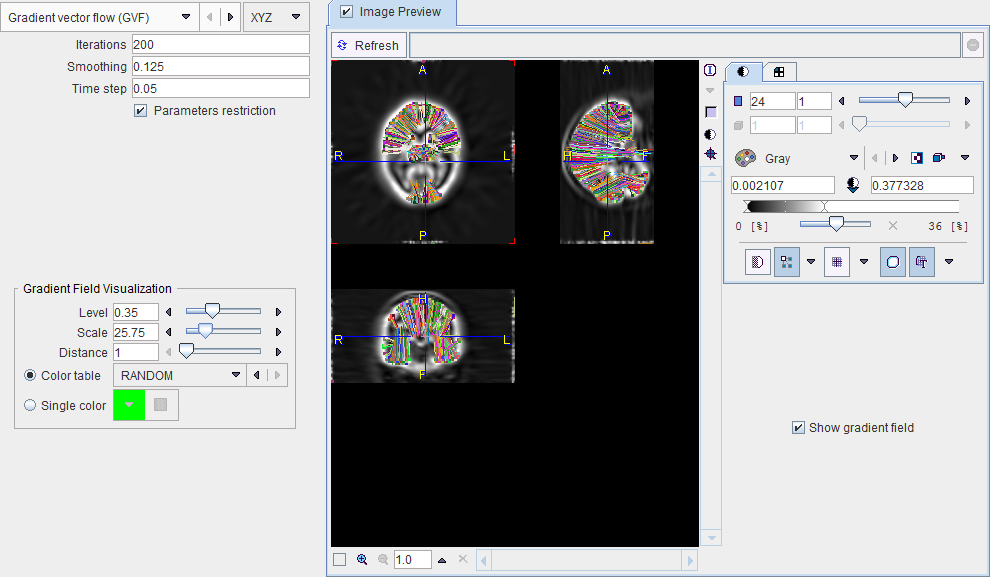
In order to guarantee algorithm convergence, the smoothing parameter and the time step should satisfy the following expression: μ<-1.36*Δt+0.22. Therefore, the Parameters restriction box should be enabled.
By enabling Image Preview and the Show gradient field, the gradient vectors can be visualized.
Reference
1.Chenyang Xu, Jerry L. Prince. Snakes, Shapes and Gradient Vector Flow, Transactions on Image Processing, March 1998, p. 359-369.