The stereotactic normalization result is shown on the NORMALIZED page. Please verify that the normalization procedure was successful by evaluating the alignment in different parts of the brain. Particularly helpful are the iso-contour lines. The thresholds on the TEMPLATE and the NORMALIZED should be adjusted so that the lines follow the same structures. The final brain structure outlines will only be adequate if the normalization succeeded.
After successful normalization the mapping between the different image spaces is established:
▪the normalization maps the MR to the atlas space;
▪the rigid transform maps the PET to MRI space;
▪the rigid transform combined with the normalization results in a transform which maps the PET to the atlas space.
As all the transformations can be inverted, the atlas space can also be mapped to PET and the MR image space. Consequently, the brain structures which are defined in the atlas space can be mapped to the PET and MR subject space and shown in the overlay.
Atlas Selection
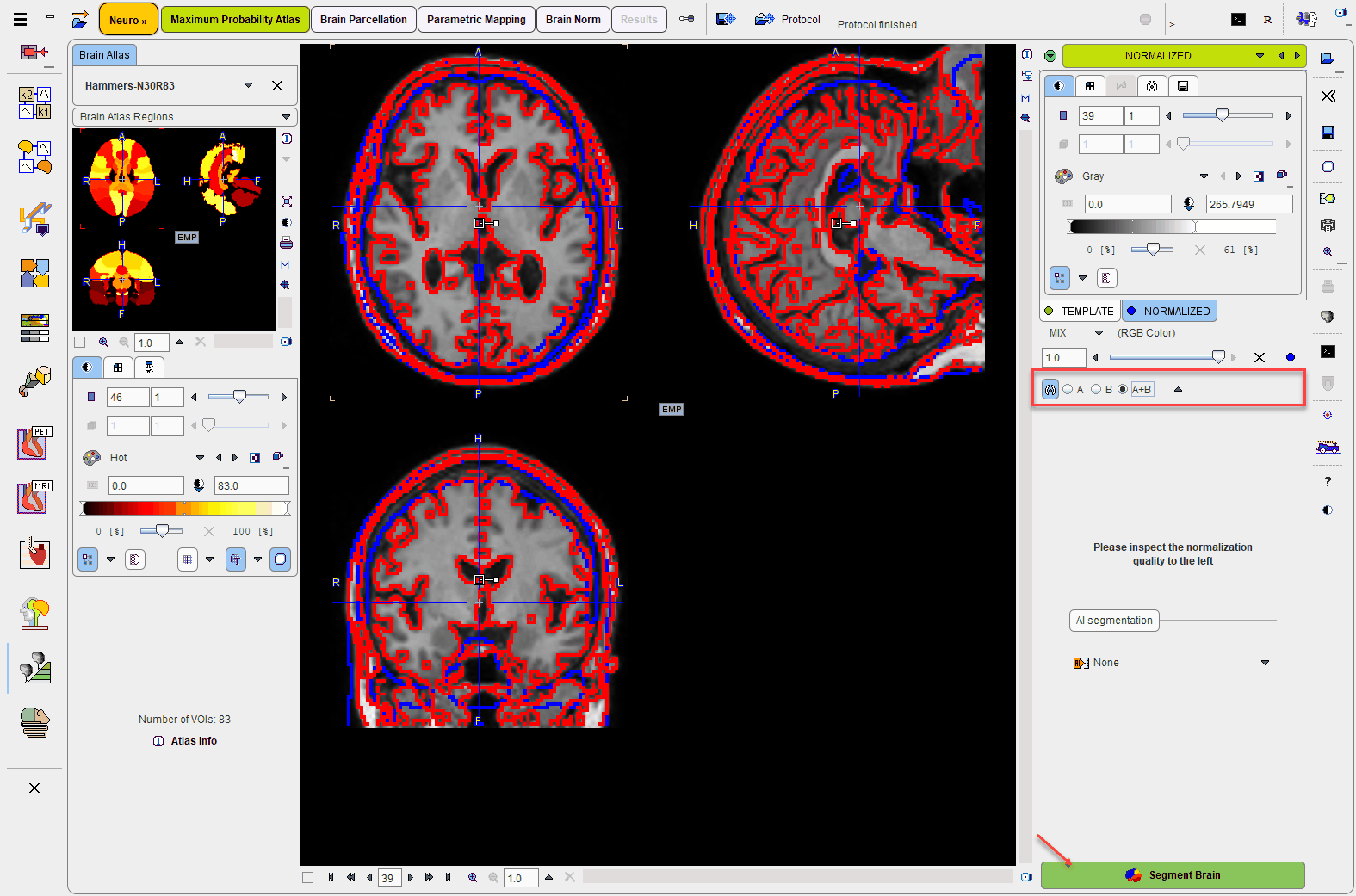
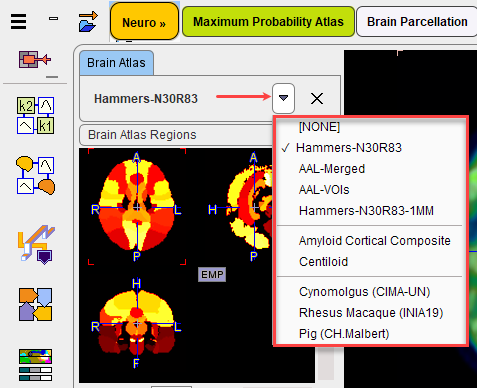
The Maximum Probability Atlas module is aimed at leveraging the brain structures defined in the N30R83 atlas. However, the same workflow can also be applied to other atlases, even to atlases defined for other species. For the selection of the atlas please activate the blue show/hide button left to NORMALIZED.
![]()
As a consequence, a window appears to the left of the page which allows selecting the atlas from a list. To hide the atlas selection window please activate the show/hide button again.
For each of the selections, the Brain Atlas Regions (defining the structures), the Brain Normalization Template (pattern for the spatial normalization), the Tissue Probability Maps and the Brain Mask of the atlas can be inspected.
Please activate the Segment Brain action button to start the mapping of the brain structures of the selected atlas.
AI Segmentation
Segmentation of the deep nuclei in the human brain data with pronounced atrophy is a known challenge. The normalization according to tissue probability maps and subsequent masking of atlas segments according to gray matter probability is widely successful in cortical regions, but can be insufficient for deep nuclei around enlarged ventricular spaces. PMOD introduces a hybrid-AI solution: it utilizes the trusted methods for cortical gray matter segmentation, but allows replacing the deep nuclei segments with the result of prediction with a trained neural network.
The option is available for selection in the AI Segmentation section of the NORMALIZED step as illustrated below:
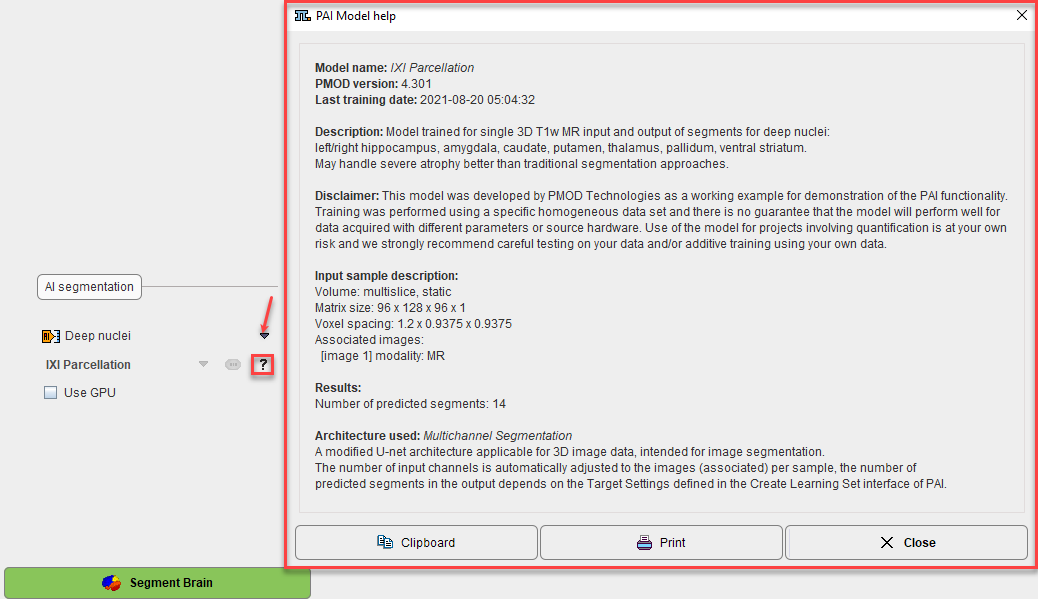
Additional information is available activating the "?" button.
Please refer to the PAI Documentation for detailed information about the the prediction-based image segmentation, as well for all information related to the infrastructure requirements.
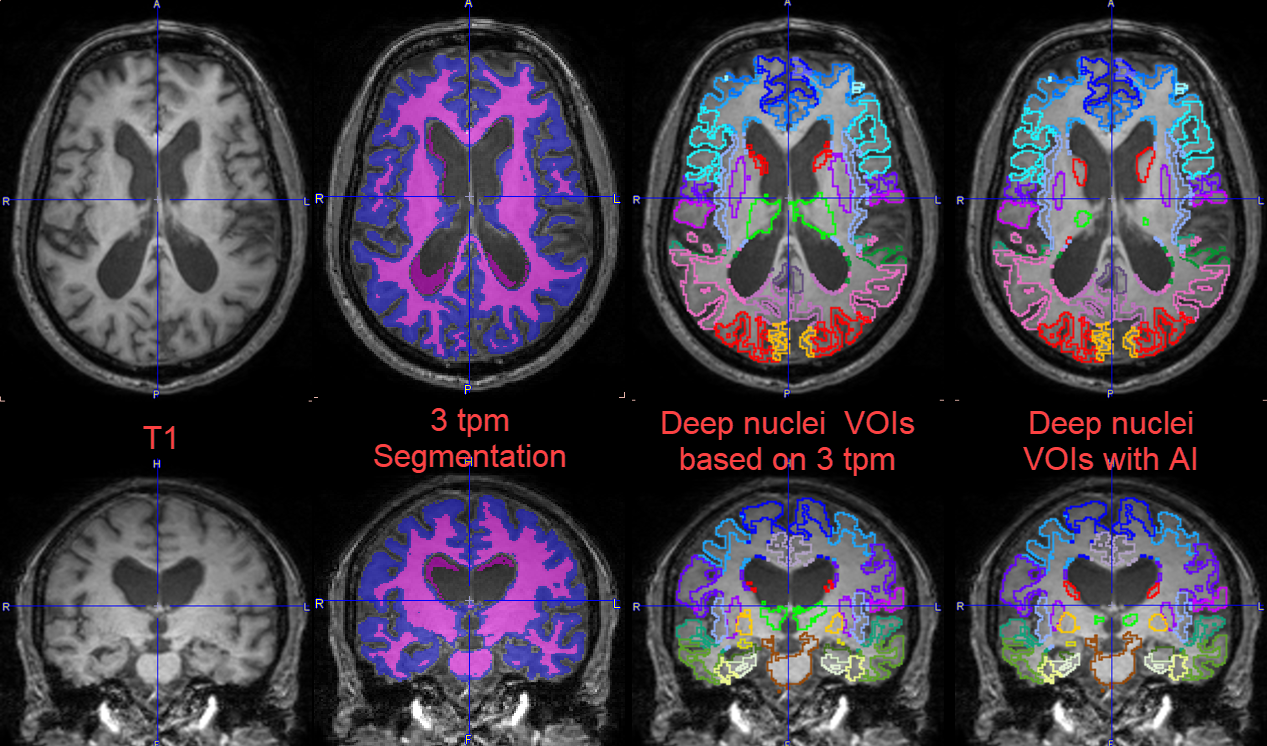
The images below illustrate the successful result for a case that was challenging for the deep nuclei segmentation using only conventional methods (3tpm segmentation). Because of the very large ventricles the deep nuclei 3 TPM based segmentation partially failed. Using the 3 TPM segmentation for the cortical gray matter and the AI prediction for the deep nuclei segments, the result is improved.