There are several segmentation methods available in the Segmentation list:
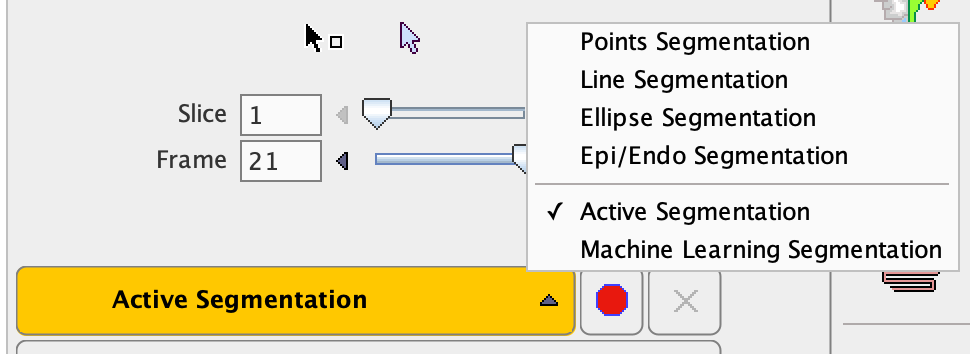
Basically, three categories of segmentations can be distinguished.
Manual Segmentations with Marker Points along Myocardium Centerline
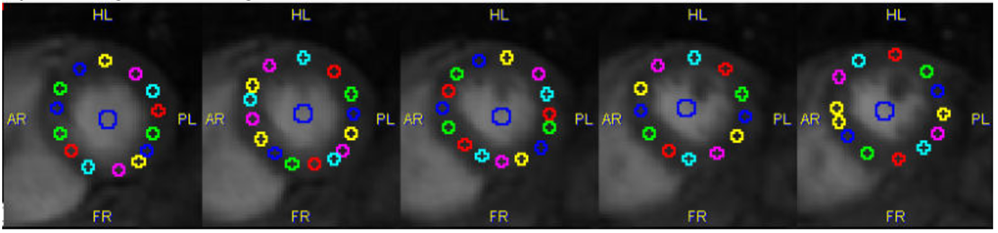
With these methods the user first has to manually place markers along the myocardium centerline in all slices covering the left ventricular wall. The example below shows a volumetric acquisition with 11 relevant slice images together with the defined markers.
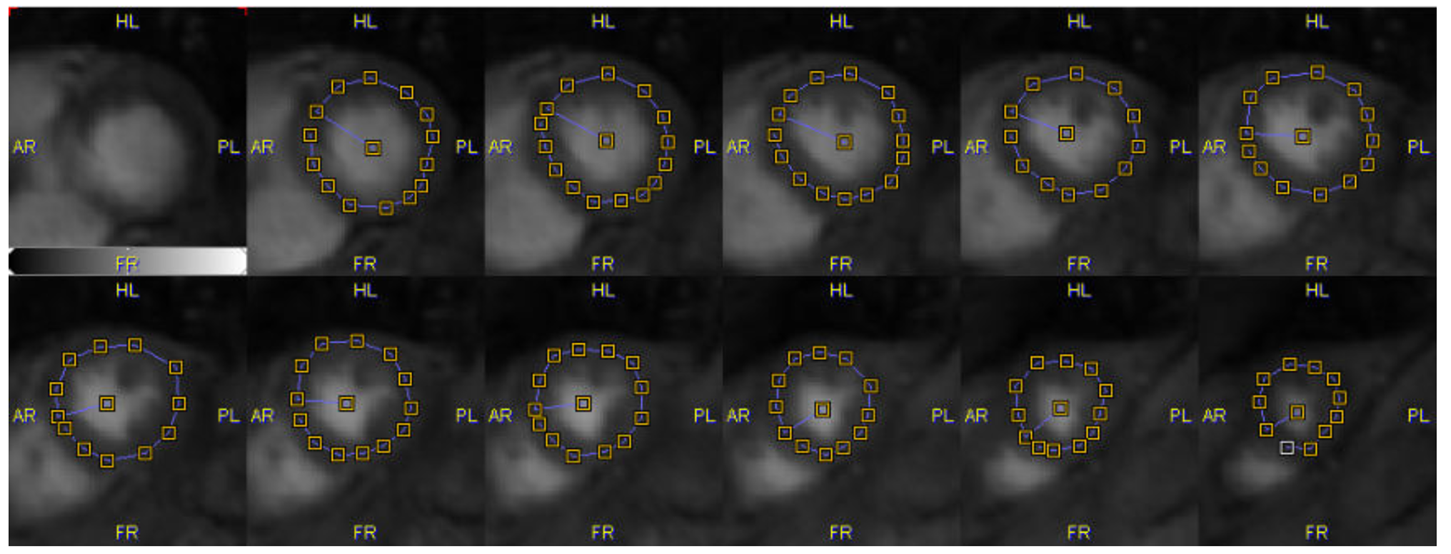
Based on these markers the segments for averaging the MR signal are derived as follows:
Points |
By creating circular regions of interest at the location of each marker. |
Line |
By connecting the markers by lines and sampling the pixels in a certain window along the lines. |
Ellipse |
By fitting an ellipse to the markers and sampling the pixels in a certain window along the ellipse.
|
Note that the Line and Ellipse segmentations result in a well-defined number of segments per slice which can be defined by the user, and for which the user has to manually define a starting point.
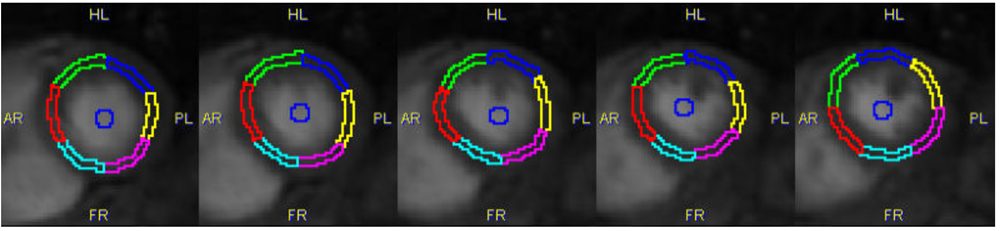
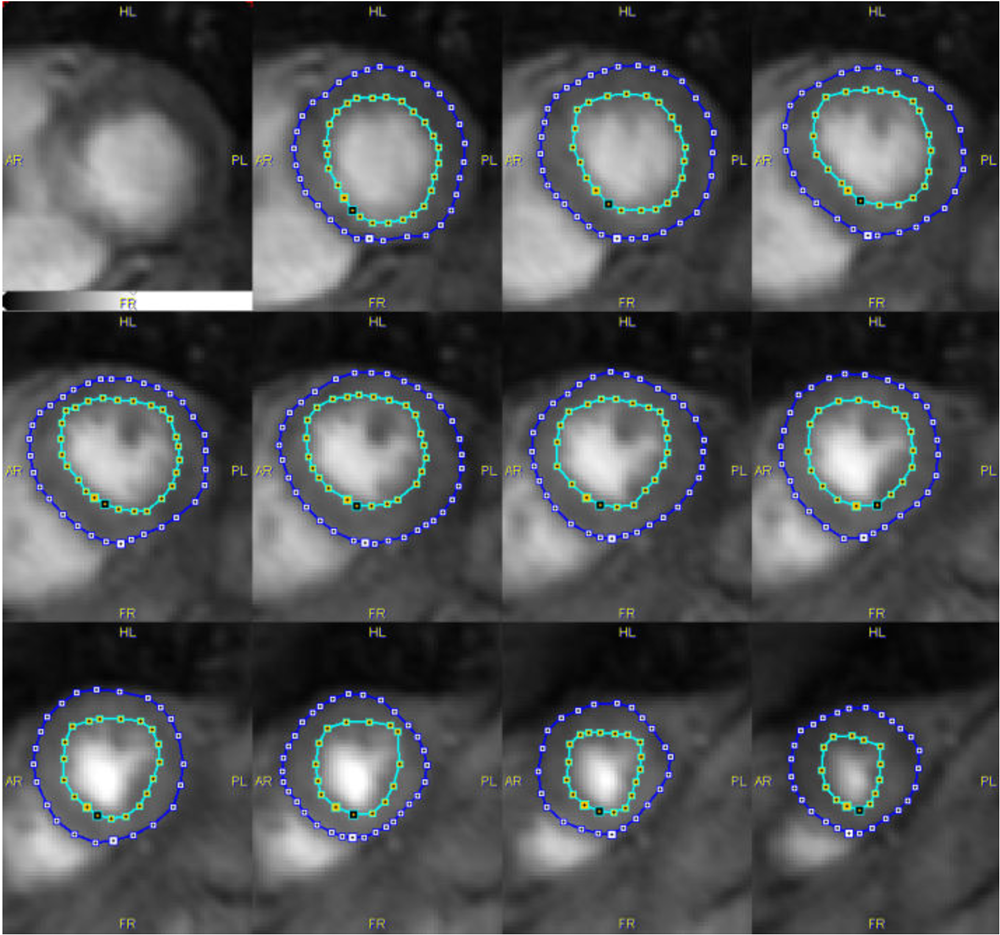
Manual Segmentation with Epi/Endo Contours
This method requires the user to manually outline the outer boundary (epicardium) and inner boundary (endocardium) of the left ventricular wall.
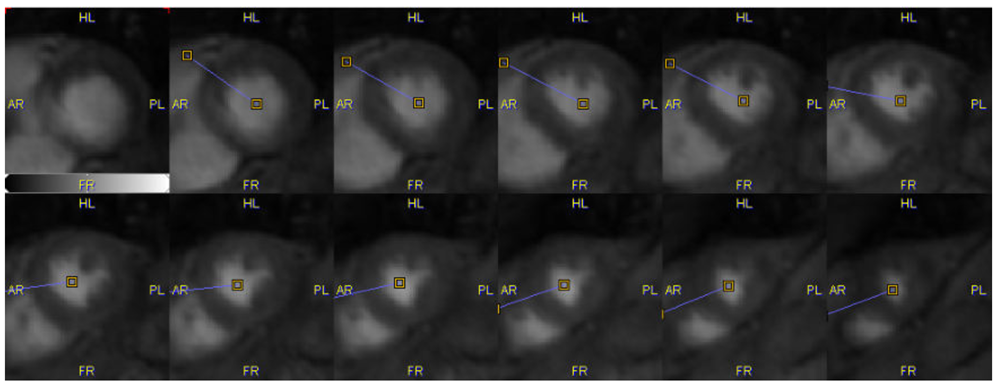
In addition he has to define a divider line by marking the LV center and the location of the RV edge:
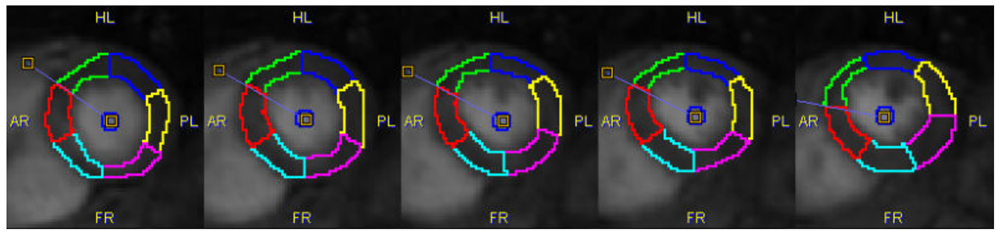
The Epi/Endo then divides the area between the two contours into a specified number of segments, resulting in a segment definition as illustrated below.
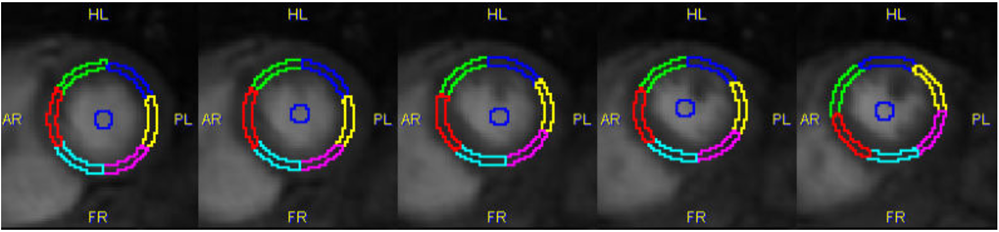
Automatic Segmentation with Active Contours
This method is experimental. It also requires markers along the centerline and tries to automatically detect the epi-and endocardial boundaries. Please refer to the online ? for some additional hints.